
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

6 Oral Region
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Understand the regions and boundaries of the oral cavity
Know the major anatomic features of the lips, cheeks, and gingivae Describe the external features of the tongue
Outline the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue and their movements Describe the hard and soft palate and their anatomic features
Describe the anatomyof the oral cavityrelated to the soft palate
Know the muscles of the soft palate, their movements, and their innervation Outline the vascular supplyand innervation of the palate
Describe the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual salivaryglands, including their vascular supplyand innervation
36 / 425

GUIDE
Head and Neck: Oral Region
Oral Cavity
page 30 page 31
Divided into two regions
Oral vestibule
Narrow space between teeth and gingival and lips and cheeks
Size controlled byorbicularis oris, buccinator, risorius, and muscles controlling lips
Contains frenula (singular: frenulum)-midline mucosal folds from upper and lower lips to the gums
Oral cavityproper
Boundaries
Anteriorly: lips
Posteriorly: oropharyngeal isthmus to oropharynx
Roof: hard palate anteriorlyand soft palate posteriorly
Floor: mucosa beneath the tongue
 Space occupied bytongue Anatomical features of the lips
Space occupied bytongue Anatomical features of the lips
Contain
Orbicularis oris muscle, and fibers of levator labii superioris, depressor anguli oris, zygomaticus major and risorius muscles Superior and inferior labial arteries and veins
a.From infraorbital and facial vessels superiorly
b.From facial and mental vessels inferiorly
Branches of infraorbital nerves (cranial nerve [CN] V2) superiorly
Branches of mental nerves (CN V3) inferiorly
Vermilion border: transition zone (border) of lip
Nasolabial grooves from nose to just lateral of angle of mouth separated lips from cheek
Philtrum: depression from nasal septum to vermilion border of upper lip
Labiomental groove separates lower lip from chin
Labial frenula: midline mucosal folds with a free edge that extend from upper and lower lips to the gums
Anatomical features of the cheeks
Lateral walls of oral cavity
Form zygomatic prominences over zygomatic bones
Principal muscle is buccinator
Buccal fat pad external to buccinator
Supplied bybuccal branches of maxillaryartery
Innervated bybuccal branches of mandibular nerve (CN V3)
Gingivae
Composed of fibrous tissue covered bymucous membrane
Firmlyattached to alveolar processes of mandible and maxilla and necks of teeth
Tongue
37 / 425
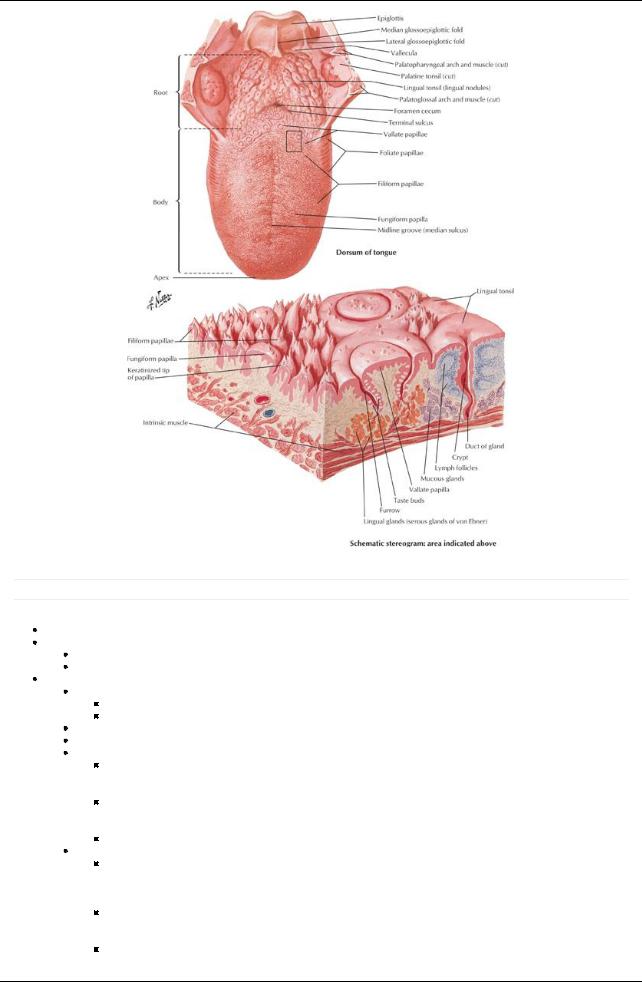
[Plate 58, Tongue]
page 31
page 32 page 32
page 33
Highlymobile organ composed largelyof muscle
Main functions
Pressing food into the pharynxduring swallowing
Assisting in the formation of words during speech
External features of the tongue anterior to sulcus terminalis
Root
Posterior one third
Attached to hyoid bone and mandible
Body: anterior two thirds
Apexor tip: pointed or rounded anterior end
Dorsum of tongue
V-shaped groove: sulcus terminalis
a.Divides tongue into oral and pharyngeal parts
b.Apexpoints to foramen cecum
Foramen cecum
a.Small pit
b.Remnant of embryonic thyroglossal duct
Numerous papillae of different types
Lingual papillae
Vallate
a.Anterior to sulcus terminalis
b.Large and flat-topped
c.Have taste buds
Foliate
a.Small folds on lateral side of tongue
b.Have taste buds
Filiform
a.Numerous and mainlyarranged in rows parallel to sulcus terminalis
b.Sensitive to touch
38 / 425

Fungiform
a.Mushroom-shaped
b.Found on tip and sides of tongue
c.Have taste buds
External features of the tongue posterior to sulcus terminalis
Posterior to palatoglossal arches
Roughened surface due to underlying lymphatic follicles = lingual tonsil
External features of inferior tongue
Lingual frenulum
Midline fold of mucosa from gingivae to posteroinferior surface of tongue
Connects tongue to floor of mouth
Sublingual caruncle
Papilla on either side of frenulum
Opening of duct of submandibular gland
Muscles
Both intrinsic and extrinsic muscles are paired
All muscles act coordinately
Fibrous septum separates muscles of each half of tongue
Extrinsic muscles
Alter position of tongue
Genioglossus
a.Most of bulk of tongue
b.Contributes to protrusion of tongue
c.Moves tongue from side to side
Hyoglossus
a.Depresses tongue
b.Aids in retraction
Styloglossus
a.Mingles with fibers of hyoglossus
b.Creates central trough or furrow with genioglossus during swallowing
c.Retracts tongue and curls side
Palatoglossus
a.Largelya soft palate muscle
b.Elevates posterior tongue
Intrinsic
Alter shape of tongue
Superior longitudinal: curls tip of tongue superiorly
Inferior longitudinal
a.Curls tip of tongue inferiorly
b.Acts with superior longitudinal muscle to shorten and thicken tongue
Transverse: narrows tongue and increases height
Vertical: flattens and broadens tongue
Vasculature
Arterial supply
Principallyfrom lingual artery, branch of external carotid
Dorsal lingual artery
Deep lingual artery
Sublingual artery
Minor contributions from tonsillar and ascending pharyngeal arteries
Venous drainage
Accompanies arterial supply
Dorsal lingual veins
Deep lingual veins (join sublingual veins)
All drain, either directlyor indirectlyto internal jugular vein
Lymphatic drainage takes one of four routes
Tip (apex) to submental nodes
Anterior medial two thirds to inferior deep cervical nodes
Anterior lateral two thirds to submandibular nodes
Posterior one third to superior deep cervical nodes
Innervation:
All muscles of tongue except palatoglossus supplied byhypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
Palatoglossus supplied bypharyngeal plexus (CN IXvia CN X)
Sensoryto anterior two thirds of tongue
General sensory: lingual nerve (CN V3)
Special sensory(taste): corda tympani (CN VII)
General and special sensoryto posterior one third of tongue: glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
39 / 425
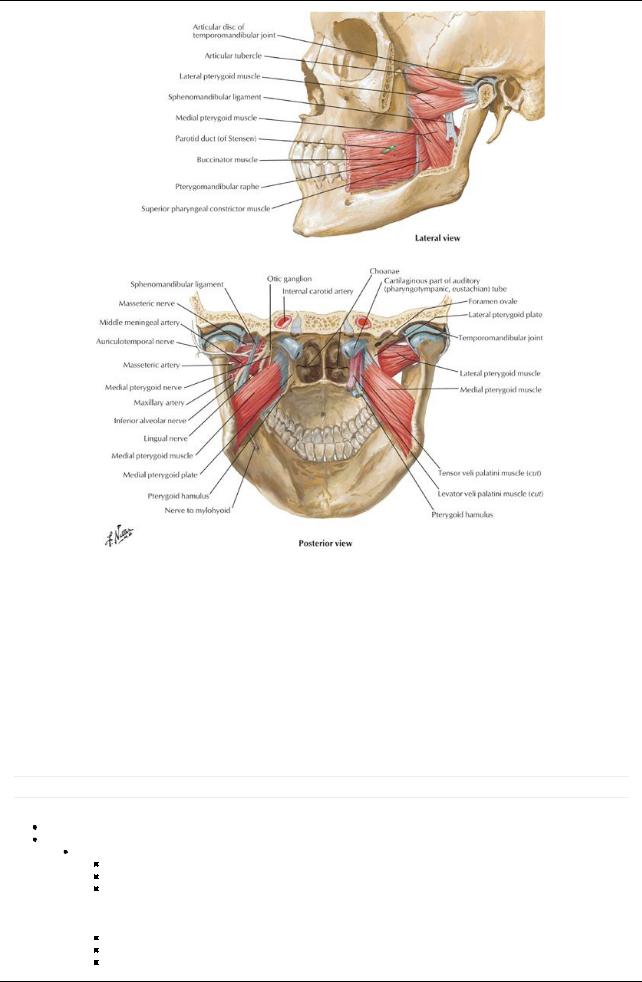
[Plate 55, Muscles Involved in Mastication (Continued)]
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Main Actions |
Genioglossus |
Mental spine of |
Dorsum of |
Hypoglossal |
Sublingual and submental arteries |
Depresses and |
|
mandible |
tongue and |
nerve |
|
protrudes tongue |
|
|
hyoid bone |
|
|
|
Hyoglossus |
Bodyand greater |
Lateral and |
Hypoglossal |
Sublingual and submental arteries |
Depresses and |
|
horn of hyoid |
inferior aspect |
nerve |
|
retracts tongue |
|
bone |
of tongue |
|
|
|
Styloglossus |
Styloid process |
Lateral and |
Hypoglossal |
Sublingual artery |
Retracts tongue and |
|
and stylohyoid |
inferior aspect |
nerve |
|
draws it up for |
|
ligament |
of tongue |
|
|
swallowing |
Palatoglossus |
Palatine |
Lateral aspect |
Vagus nerve |
Ascending pharyngeal arteries and |
Elevates posterior |
|
aponeurosis of |
of tongue |
and pharyngeal |
Palatine branches of facial and |
tongue |
|
soft palate |
|
plexus |
maxillaryarteries |
|
Palate
page 33
page 34 page 34
page 35
Forms roof of mouth and floor of nasal cavities
Consists of two parts
Hard palate anteriorly
Formed from bypalatine processes of maxillae and horizontal plates of palatine bones
Covered with periosteum and oral mucosa (inferiorly) and respiratorymucosa superiorly
Has five foramina
a.Incisive fossa behind central incisors transmits nasopalatine nerves via incisive canals
b.Paired greater palatine foramina medial to third molar transmits greater palatine vessels and nerves
c.Paired lesser palatine foramina posterior to greater palatine foramina transmits lesser palatine nerves and vessels
Mucous secreting palatine glands beneath mucosa Incisive papilla directlyposterior to maxillaryincisors Palatine raphe
a. Midline ridge/groove
40 / 425

b. Represents line of fusion of embryonic palatal plates Soft palate posteriorly
Moveable posterior third suspended from hard palate
No bonyskeleton
Attaches to hard palate via aponeurotic palate
a.Expanded tendineus aponeurosis of tensor veli palatini muscles
b.Thick anteriorly
Muscular palate (tensor veli palatini) posteriorly
Posterior curved free margin has conical projection: uvula
Anatomical features related to the soft palate
Arches
Join soft palate to tongue and pharynx
Palatoglossal arch
a.Mucosal fold
b.Contains palatoglossus muscle
Palatopharyngeal arch
a.Mucosal fold
b.Posterior to palatoglossal arch
c.Contains palatoglossus muscle
Form anterior and posterior boundaries of tonsillar fossa on either side
Tonsillar fossae
Contain palatine tonsils
Masses of lymphoid tissue between arches
Fauces
Term for passage from oral cavityto oropharynx
Bounded by
a.Soft palate superiorly
b.Root of tongue inferiorly
c.Palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches laterally
Muscles of soft palate
Four paired muscles descend from base of brain to palate
Levator veli palatine elevates soft palate during swallowing, opens auditorytube
Tensor veli palatini tenses soft palate during swallowing
Palatoglossus elevates posterior tongue
Palatopharyngeus tenses soft palate and pulls pharynxsuperiorlyand anteriorlyduring swallowing
 Unpaired musculus uvulae shortens uvula Swallowing and the palate
Unpaired musculus uvulae shortens uvula Swallowing and the palate
Complexmechanism
Soft palate tenses to allow tongue to press against it
Tongue squeezes bolus of food to back of oral cavity
 Soft palate elevates superiorlyand posteriorlyto prevent back flush of food into nasal cavity Arterial supply
Soft palate elevates superiorlyand posteriorlyto prevent back flush of food into nasal cavity Arterial supply
Branches of descending palatine arteryon each side
Greater palatine artery
Lesser palatine artery
 Ascending palatine arteryfrom facial artery Venous drainage via pterygoid venous plex Lymphatic drainage: deep cervical nodes Innervation
Ascending palatine arteryfrom facial artery Venous drainage via pterygoid venous plex Lymphatic drainage: deep cervical nodes Innervation
Sensoryfrom pterygopalatine ganglion (from CN V2)
Greater palatine nerve to hard palate
Nasopalatine nerve to anterior hard palate
Lesser palatine nerve to soft palate
Motor
Tensor veli palatini innervated bymedial pterygoid nerve from otic ganglion (CN V3)
All other muscles bycranial root of spinal accessorynerve (CN XI) via pharyngeal plexus
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
InnervationBlood supply |
Main actions |
|
Levator veli |
Temporal (petrous |
Palatine |
Vagus |
Ascending palatine artery |
Elevates soft palate during |
palatini |
portion) bone |
aponeurosis |
nerve via |
branch of facial arteryand |
swallowing |
|
|
|
pharyngeal |
descending palatine artery |
|
|
|
|
plexus |
branch of maxillaryartery |
|
Tensor veli |
Scaphoid fossa of |
Palatine |
Mandibular |
Ascending palatine artery |
Tenses soft palate and |
palatini |
medial pterygoid plate, |
aponeurosis |
nerve |
branch of facial arteryand |
opens auditorytube during |
|
spine of sphenoid, and |
|
|
descending palatine artery |
swallowing and yawning |
|
auditorytube |
|
|
branch of maxillaryartery |
|
Palatopharyngeus |
Hard palate and superior |
Lateral |
Vagus |
Ascending palatine artery |
Tenses soft palate; pulls |
|
palatine aponeurosis |
pharyngeal |
nerve via |
branch of facial arteryand |
walls of pharynxsuperiorly, |
|
|
wall |
pharyngeal |
descending palatine artery |
anteriorly, and medially |
|
|
|
plexus |
branch of maxillaryartery |
during swallowing |
Musculus uvulae |
Nasal spine and palatine |
Mucosa of |
Vagus |
Ascending palatine artery |
Shortens, elevates, and |
|
aponeurosis |
uvula |
nerve via |
branch of facial arteryand |
retracts uvula |
|
|
|
pharyngeal |
descending palatine artery |
|
|
|
|
plexus |
branch of maxillaryartery |
|
Salivary Glands
41 / 425
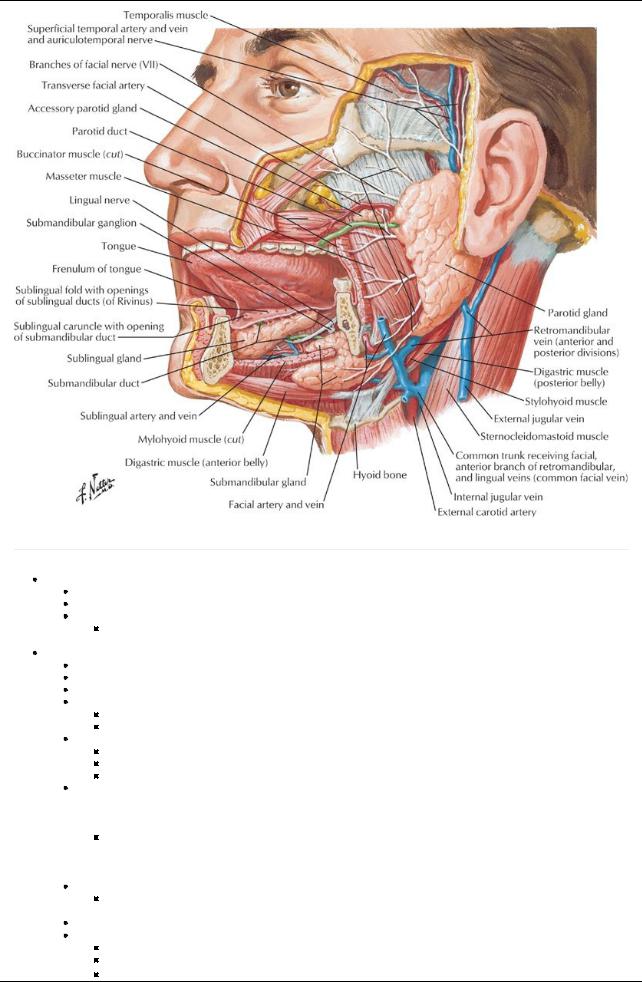
[Plate 61, Salivary Glands]
page 35 page 36
Functions
Moisten and lubricate food
Begin digestion of starches
Contribute to
Abilityto taste
 Prevention of tooth decay Parotid gland:
Prevention of tooth decay Parotid gland:
Largest salivarygland
Thin waterysecretion
Found within investing cervical fascia
Occupies space between ramus of mandible and anterior border of sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle
Overlaps posterior masseter muscle
Deep part extends posteriorlyto mastoid process and external auditorymeatus
Parotid duct
Emerges at anterior border of gland
Runs over masseter
Pierces buccinator to enter mouth opposite upper second molar
Structures passing through the gland  Facial nerve
Facial nerve
a.Enters gland and branches into two stems
b.Two stems give rise to five branches that emerge from borders of gland
Superficial temporal vein
a.Runs through deeper part of gland
b.Unites with maxillaryvein within the gland to form retromandibular vein
 External carotid arterythrough deep part of gland Arterial supply
External carotid arterythrough deep part of gland Arterial supply
External carotid artery
 Superficial temporal arteries Venous drainage: retromandibular vein Innervation
Superficial temporal arteries Venous drainage: retromandibular vein Innervation
Great auricular nerve (C2 and C3 spinal nerves)
Auriculotemporal nerve (CN V3)
Parasympathetic fibers from glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) via auriculotemporal from otic ganglion
42 / 425

Sympathetic fibers from external carotid plexus from cervical ganglia
Submandibular gland
Lies superior and inferior to posterior half of mandible
Divided into superficial and deep parts bymylohyoid muscle
Duct
Opens at sublingual papilla, one on either side of lingual frenulum
Lingual nerve loops under duct
Arterial supply: submental artery
Innervation
Secretomotor parasympathetic fibers
a.Presynaptic fibers from facial nerve via chorda tympani to submandibular ganglion
b.Postsynaptic fibers from cells in submandibular ganglion
Vasoconstrictive sympathetic fibers from superior cervical ganglion
Sublingual glands
Smallest and deepest of glands
Lie in floor of mouth within sublingual folds, between mandible and genioglossus muscle
Numerous ducts open along sublingual folds
Arterial supply
Sublingual arteryfrom lingual artery
Submental arteryfrom facial artery
Innervation same as that for submandibular gland
43 / 425
