
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

3 Superficial Face
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Outline the main muscles of facial expression and their actions
Know the layers of the scalp, its innervation and vascular supply
Understand the vascular supplyand lymphatic drainage of the face
Know the sensoryand motor innervation of the face
Outline the main muscles of mastication and their actions
17 / 425
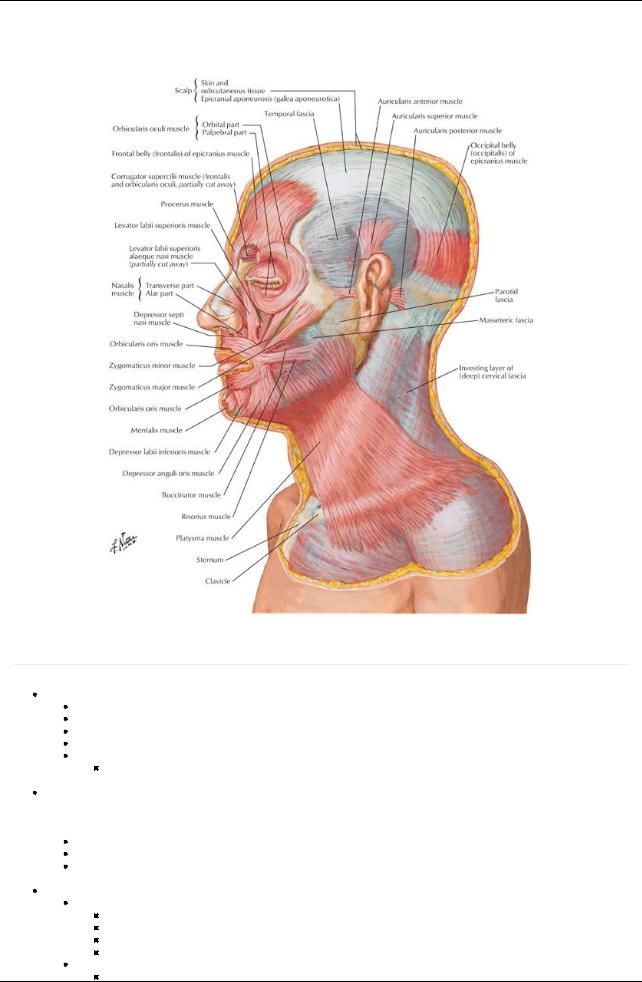
GUIDE
Head and Neck: Superficial Face
[Plate 25, Muscles of Facial Expression: Lateral View]
Face
page 12
page 13
Subcutaneous tissue of face
Contains muscles of facial expression
Contains varying amount of fat-for example, buccal fat pads of the cheek
Highlyvascular
Contains sensorybranches of trigeminal (V) nerve, upper cervical spinal nerves and motor branches of the facial nerve (VII)
Traversed byskin ligaments (retinacula cutis)
Bands of connective tissue
 Connect skin to bones Muscles of facial expression
Connect skin to bones Muscles of facial expression
The muscles of facial expression are in several ways unique among the skeletal muscles of the body. Theyall originate embryologically from the second pharyngeal arch and are all innervated byterminal branches of the facial nerve (cranial nerve [CN] VII).Additionally, most arise from the bones of the face or fascia, and insert into the dermis of the skin overlying the scalp, face, and anterolateral neck.
Lie within superficial fascia
Most arise from bone and insert into skin
Arranged as sphincters or dilators around orifices of face
 Innervated byone of five main branches of facial nerve (occipitalis innervated byposterior auricular branch) Muscles related to the orbit
Innervated byone of five main branches of facial nerve (occipitalis innervated byposterior auricular branch) Muscles related to the orbit
Orbicularis oculi
Composed of three parts: lacrimal, palpebral, orbital
Lacrimal part draws eyelids and lacrimal puncta mediallyto drain tears
Inner palpebral part gentlycloses eyelids (blinking)
Outer orbital part that tightlycloses eyelids (squinting)
Corrugator supercilii
Draws medial end of eyebrow mediallyand inferiorlyfor a concerned look
18 / 425

Wrinkles skin of forehead
Frontalis portion of occipitofrontalis
Elevates the eyebrows for a surprised look
Wrinkles the forehead
Muscles related to the nose
Nasalis
Consists of compressor naris-compresses nostril
And dilator naris-flares nostrils
Procerus
From forehead over bridge of nose
Draws medial eyebrow inferiorly
Creates transverse wrinkles over nose-frowning
Muscles related to the ear
Anterior, superior, and posterior auricular
Variablydeveloped
Muscles related to mouth and lips
Orbicularis oris
Sphincter of the mouth
Important for speech, holding food between the teeth, whistling, blowing
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
Elevates nose and upper lip
Mentalis
Wrinkles skin on chin
Buccinator
Involved in smiling
Holds food between teeth during chewing
Used in whistling, sucking, and horn blowing
Depressor anguli oris
Depresses angle of mouth
Levator anguli oris
Elevates corner of mouth
Levator labii superioris
Lifts and everts upper lip
Depressor labii inferioris
Draws lip down and laterally
Used to show impatience
Risorius
Draws corner of mouth laterally
Used in grinning
Zygomaticus major
Draws angle of mouth up and laterally
Used in smiling and laughing
Zygomaticus minor
Raises upper lip as when showing contempt
Platysma
Depresses mandible
Draws corners of mouth down
Used when grimacing
Scalp
page 13
page 14
Extends from superior nuchal line to superior orbital ridge
Laterallyextends to external acoustic meatus and zygomatic arch
Composed of five layers
First three are adherent to skull, move as one
Skin (1)
Contains sweat and sebaceous glands and hair follicles
Well vascularized
Connective Tissue (2)
Dense
Well vascularized and innervated
Aponeurosis of occipitofrontalis muscle (3)
Tendinous sheet
Connects occipitalis, frontalis and superior auricular muscles
Loose connective tissue (4)
Spongy
Layer that collects fluid from injuryof infection
Moves freelywith first three layers over pericranium
Periosteum of skull (5)
External periosteum of calvaria
Fairlyfirmlyattached to bone
Most tightlybound at suture lines
Vasculature of scalp
Scalp has rich blood supply, so bleeding from a scalp injuryis profuse
Arteries anastomoses
Branches of external carotid arteryto scalp
19 / 425

Posterior auricular
Occipital
Superficial temporal
Branches of internal carotid arteryto scalp
Supratrochlear artery
Supraorbital artery
Venous drainage of scalp via veins of same name accompanying arteries
Deep aspects of scalp drain to deep temporal veins to pterygoid venous plexus
Innervation of scalp
Anterior to auricle: ophthalmic, maxillaryand mandibular divisions of cranial nerve (CN) V(trigeminal)
Posterior to auricle: cutaneous branches from C2 and C3 spinal nerves
Vascular supply of the face
Arteries
Facial artery
Major arterial source for face
Arises from external carotid artery, crosses mandible and traverses face to medial angle of eye
Branches to upper and lower lip and nose
Superficial temporal artery
Terminal branch of external carotid
Enters temporal fossa and ends in scalp
Transverse facial artery
From superficial temporal
Crosses face below zygomatic arch
Veins
Supratrochlear vein
Descends from forehead to nose
Joins supraorbital to form angular vein
Supraorbital vein
Begins in forehead and passes mediallyto join supratrochlear vein
Sends branch through supraorbital notch to joint superior ophthalmic vein
Facial vein
Two veins provide main venous drainage of face
Follow course of facial artery
Drain directlyor indirectlyinto internal jugular vein
Communicates with pterygoid venous plexus and cavernous sinus via superior ophthalmic vein
Superficial temporal vein
Drains scalp and forehead
Unites with maxillaryvein to form retromandibular vein
Retromandibular vein
Descends through parotid gland
Sends branch to facial vein
Joins posterior auricular vein to form external jugular vein
page 14 page 15
Lymphatic drainage of the face
Superficial lymphatics travel with veins
Deep lymphatics travel with arteries
Lateral face → parotid lymph nodes
Upper lip and lateral lower lip → submandibular lymph nodes
Chin and central part of lower lip → submental lymph nodes
All lymphatic drainage eventuallyreaches the deep cervical lymph nodes
Innervation of the face
Cutaneous branches of the cervical nerves
From the cervical plexus
Innervate posterior neck, ear, and area over parotid gland
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Sensoryfor the face
Motor for muscles of mastication
Branches of ophthalmic nerve-CN V1
Nasociliarynerve → external nasal nerve to skin on dorsum of nose
Nasociliarynerve → infratrochlear nerve to skin and lower eyelid
Frontal nerve → supratrochlear nerve to skin in midforehead
Frontal nerve → supraorbital nerve to skin of forehead and upper eyelid
Branches of maxillarynerve-CN V2
Infraorbital nerve to skin of cheek, lower lid, lateral nose and mouth, upper lip
Zygomaticotemporal nerve to skin over anterior temple
Zygomaticofacial nerve to skin over zygomatic arch
Branches of mandibular nerve-CN V3
Auriculotemporal nerve-to skin of external ear, posterior temple, anterior to ear
Buccal nerve-to skin of cheek
20 / 425

Mental nerve-to skin of chin and lower lip
Facial nerve
Sole motor supplyto muscles of facial expression
Has five main branches
Temporal
Zygomatic
Buccal
Mandibular
Cervical
Names refer to areas theysupply
page 15
page 16
Other muscles associated with the face: Muscles of mastication
The muscles of mastication include four pairs of muscles (left and right side) that attach to the mandible, are embryological derivatives of the first pharyngeal arch, are all innervated bythe mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3), and are important in biting and chewing food.
All attach to mandible
Responsible for biting and chewing (movements at the temporomandibular joint [TMJ]) All innervated bybranches of the mandibular nerve (CN V3)
All supplied bybranches of the maxillaryartery Group of four muscles
Temporalis
Large, fan-shaped
Covers most of the side of the head
Inserts on coronoid process of mandible
Masseter
Deep to parotid gland and crossed byparotid duct
Inserts on entire lateral surface of ramus of mandible except for condylar process
Lateral pterygoid
Deep to temporal muscle
Runs horizontallybackwards from infratemporal fossa and lateral pterygoid plate to insert on mandible
Covered with dense pterygoid plexus of veins
Medial pterygoid
Covered byinferior fibers of lateral pterygoid
Runs from inner surface of lateral pterygoid plate inferiorlyto inner surface of ramus of mandible
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Main Actions |
Nerve Supply |
Blood Supply |
Temporalis |
Floor of temporal fossa |
Coronoid |
Elevates mandible; posterior |
Mandibular |
Superficial temporal and |
|
and deep temporal fascia |
process and |
fibers retrude mandible |
nerve (V3)-deep |
maxillaryarteries, middle, |
|
|
ramus of |
|
temporal nerves |
anterior, and posterior |
|
|
mandible |
|
|
deep temporal arteries |
Masseter |
Zygomatic arch |
Ramus of |
Elevates and protrudes |
Mandibular |
Transverses facial artery; |
|
|
mandible |
mandible; deep fibers retrude it |
nerve (V3)- |
masseteric branch of |
|
|
and coronoid |
|
masseteric |
maxillaryand facial |
|
|
process |
|
nerve |
arteries |
Medial |
Superior head: |
Neck of |
Acting together, protrude |
Mandibular |
Facial and maxillary |
pterygoid |
infratemporal surface of |
mandible, |
mandible and depress chin; |
nerve (V3)-nerve |
arteries |
|
greater wing of sphenoid |
articular disc, |
acting alone and alternately, |
to medial |
|
|
Inferior head: lateral |
and capsule |
produces side-to-side |
pterygoid |
|
|
pterygoid plate |
of TMJ |
movements |
|
|
Lateral |
Infratemporal surface of |
Pterygoid |
Together, protrude mandible, |
Mandibular |
Maxillaryartery-muscular |
pterygoid |
greater wing of sphenoid |
fovea, |
depress chin |
nerve (V3)- |
branches |
|
and lateral surface of |
capsule of |
Alone and alternately, side to |
muscular |
|
|
lateral plate of pterygoid |
TMJ and |
side grinding |
branches from |
|
|
plate |
articular disk |
|
anterior division |
|
21 / 425
