
- •Contents
- •Acknowledgements
- •Introduction
- •How to use this book
- •Glossary of grammatical terms
- •A note on Chinese characters
- •1. Overview of pronunciation and Pinyin romanization
- •2. Syllable, meaning, and word
- •3. The Chinese writing system: an overview
- •4. Phrase order in the Mandarin sentence
- •5. Nouns
- •6. Numbers
- •9. Noun phrases
- •10. Adjectival verbs
- •11. Stative verbs
- •12. Modal verbs
- •13. Action verbs
- •14. Prepositions and prepositional phrases
- •15. Adverbs
- •16. Conjunctions
- •17. The passive
- •18. Names, kinship terms, titles, and terms of address
- •19. Introductions
- •20. Greetings and goodbyes
- •21. Basic strategies for communication
- •22. Telecommunications and e-communications: telephones, the internet, beepers, and faxes
- •23. Negating information
- •24. Asking questions and replying to questions
- •26. Describing people, places, and things
- •27. Describing how actions are performed
- •28. Indicating result, conclusion, potential, and extent
- •29. Making comparisons
- •30. Talking about the present
- •31. Talking about habitual actions
- •32. Talking about the future
- •33. Indicating completion and talking about the past
- •34. Talking about change, new situations, and changing situations
- •35. Talking about duration and frequency
- •36. Expressing additional information
- •37. Expressing contrast
- •38. Expressing sequence
- •39. Expressing simultaneous situations
- •40. Expressing cause and effect or reason and result
- •41. Expressing conditions
- •42. Expressing ‘both,’ ‘all,’ ‘every,’ ‘any,’ ‘none,’ ‘not any,’ and ‘no matter how’
- •43. Expressing location and distance
- •44. Talking about movement, directions, and means of transportation
- •45. Talking about clock time and calendar time
- •46. Expressing obligations and prohibitions
- •47. Expressing commands and permission
- •48. Expressing ability and possibility
- •49. Expressing desires, needs, preferences, and willingness
- •50. Expressing knowledge, advice, and opinions
- •51. Expressing fear, worry, and anxiety
- •52. Expressing speaker attitudes and perspectives
- •53. Topic, focus, and emphasis
- •54. Guest and host
- •55. Giving and responding to compliments
- •56. Expressing satisfaction and dissatisfaction
- •57. Expressing gratitude and responding to expressions of gratitude
- •58. Invitations, requests, and refusals
- •59. Expressing apologies, regrets, sympathy, and bad news
- •60. Expressing congratulations and good wishes
- •Index

43
Expressing location and distance
43.1Location
43.1.1Words that indicate location and compass direction
43.1.1.1Location words
Mandarin location words consist of a base form and a location suffix. Base forms never occur alone. Some base forms occur with several different suffixes with no change in meaning. Here are the Mandarin location words and their English equivalents.
Base form |
Mandarin location words |
|
English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
|
lm |
lmtou |
lmmiàn |
lmbipn |
in |
|
/ |
|
/ |
|
wài |
wàitou |
wàimian |
wàibian |
out |
|
/ |
|
/ |
|
shàng |
shàngtou |
shàngmian |
shàngbian |
over |
|
/ |
|
/ |
|
xià |
xiàtou |
xiàmian |
xiàbian |
under |
|
/ |
|
/ |
|
qián |
qiántou |
qiánmian |
qiánbian |
in front of |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
|
hòu |
hòutou |
hòumian |
hòubian |
behind |
|
|
|
/ |
|
zun |
|
zunmiàn |
zunbian |
left |
|
|
|
/ |
|
yòu |
|
yòumiàn |
yòubian |
right |
/ |
|
/ |
|
|
duì |
|
duìmiàn |
|
across from |
|
|
/ |
/ |
|
páng |
|
duìmiàn |
pángbipn |
next to |
|
/ |
|
|
|
zhsng |
zhsngjipn |
|
|
between |
|
|
|
|
|
291

EXPRESSING LOCATION AND DISTANCE |
43.1 |
NOTES |
1 In traditional characters, the character lm is also written as . |
2The choice of suffix is determined by the region of China and the personal preference of the speaker.
3Mandarin has a second word for ‘in,’ nèi. nèi does not occur with suffixes and has very restricted in usage. It is used in fixed expressions such as:
/ |
guónèi |
domestic (vs. / guówài foreign) |
|
nèibù |
internal |
|
nèiren |
my wife |
|
|
|
43.1.1.2Compass direction
The words for north, east, south, and west are also formed with a base form and a suffix. The suffix can be miàn or / bipn.
The combination compass direction words (northeast, southwest, etc.) usually occur without a suffix. If a suffix occurs, it is miàn or / bipn.
Base form |
Mandarin compass direction words |
English |
|
|
|
|
|
/ |
/ |
/ |
|
dsng |
dsngmiàn |
dsngbian |
east |
|
|
/ |
|
nán |
nánmiàn |
nánbian |
south |
|
|
/ |
|
xr |
xrmiàn |
xr bian |
west |
|
|
/ |
|
bli |
blimiàn |
blibian |
north |
|
( )/ ( ) |
( )/ ( ) |
|
|
dsngnán (miàn) |
dsngnán (bian) |
southeast |
|
( )/ ( ) |
( )/ ( ) |
|
|
dsngbli (miàn) |
dsngbli (bian) |
northeast |
|
( ) |
( )/ ( ) |
|
|
xrnán (miàn) |
xrnán (bian) |
southwest |
|
( ) |
( )/ ( ) |
|
|
xrbli (miàn) |
xrbli (bian) |
northwest |
|
|
|
|
43.1.2Spatial orientation with respect to a reference point
43.1.2.1Indicating location with respect to a reference using location words
To indicate that something is ‘inside,’ ‘outside,’ ‘over,’ ‘under,’ etc. a reference point, use the following structure:
reference point de location word
In the following phrases, the reference point is the house. Note that de may be omitted.
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) lmtou
inside the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) wàitou outside the house
292

Location |
43.1 |
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) shàngtou
on the house/over the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) xiàtou
below the house/under the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) qiántou
in front of the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) hòutou behind the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) zunbian
to the left of the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) yòubian
to the right of the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) duìmiàn across from the house
( ) / ( ) fángzi (de) zhsngjipn between the houses
!"/ !" fángzi (de) pángbipn next to the house
The location base forms / lm ‘inside,’ wài ‘outside,’ shàng ‘above,’ and xià ‘below’ can directly follow the reference point. When they occur this way, de does not occur.
reference point + location base form |
|
( ) / ( ) or |
/ |
fángzi (de) lmtou |
fángzi lm |
inside the house |
inside the house |
( ) / ( ) or |
|
fángzi (de) wàitou |
fángzi wài |
outside the house |
outside the house |
( ) / ( ) or |
|
fángzi (de) shàngtou |
fángzi shàng |
on top of the house |
on top of the house |
( ) / ( ) or |
|
fángzi (de) xiàtou |
fángzi xià |
below the house |
below the house |
293

EXPRESSING LOCATION AND DISTANCE |
43.1 |
43.1.2.2Indicating location with compass direction words
To indicate that something is ‘east of,’ ‘west of,’ ‘north of,’ or ‘south of’ a reference point, use the following structure. Keep in mind that compass direction words can be used with the miàn or / bipn suffix.
reference point de compass direction word
|
!" |
|
|
|
||||
|
fángzi de blimiàn |
|||||||
|
north of the house |
|||||||
!" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
!" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
fángzi de xrmiàn |
|
|
|
|
|
!" |
||
west of the house |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fángzi de dsngmiàn |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
east of the house |
|
!" |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
fángzi de nánmiàn |
|||||||
|
south of the house |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.1.3Describing the location of an object
To describe the location of an object with respect to a reference point, say: object zài reference point de location word
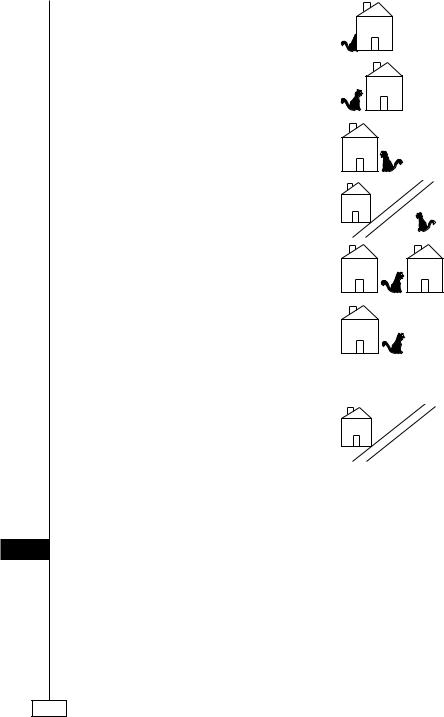
In these examples, the object is the cat, and the reference point is the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) lmtou.
The cat is inside the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) wàitou.
The cat is outside the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) shàngtou.
The cat is on the house/over the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) xiàtou.
The cat is below the house/under the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) qiántou.
The cat is in front of the house.
294
Indicating that an object exists or does not exist at a location |
43.2 |
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) hòutou.
The cat is behind the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) zunbian.
The cat is to the left of the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) yòubian.
The cat is to the right of the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) duìmiàn.
The cat is across from the house.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) zhsngjipn.
The cat is between the houses.
!( )!( )
Mpo zài fángzi (de) pángbipn.
The cat is next to the house.
Use the same pattern to indicate location in terms of compass direction:
object zài reference point de compass location word
!( ) ( )!E F E F
Fángzi zài lù (de) xrbli (bipn).
The house is to the northwest of the road.
!( ) ( )!( ) ( )
Lù zài fángzi (de) dsngnán (bipn).
The road is to the southeast of the house.
43.2Indicating that an object exists or does not exist at a location
To indicate that an object exists at a location, use the following pattern. Note thatzài is optional at the beginning of the sentence.
( zài) location ynu object
At location there is object (there are objects).
295

EXPRESSING LOCATION AND DISTANCE |
43.2 |
( ) !"# ( ) !"#
(Zài) zhuszi shàng ynu sht.
On the table there is a book (there are books).
( ) !"#$ E F !"#$
(Zài) fángzi hòubian ynu mpo.
Behind the house there is a cat (there are cats).
ynu object zài location
There is object (there are objects) at location.
!"#$%&!"#$%&
Ynu likng bln sht zài zhuszi shàng.
There are two books on the table.
!"#$%&'(!"#$%&'(
Ynu yrzhr mpo zài fángzi de hòubian.
There is a cat behind the house.
To indicate that an object does not exist at a location, use the following structure:
( zài) location méi ynu object At location there is no object.
( ) !"#$ ( ) !"#$
(Zài) fángzi lm méi ynu rén.
There are no people in the house.
(lit. ‘In the house there are no people.’)
( ) !"#$ ( ) !"#$
(Zài) wtzi lm méi ynu zhuszi.
There aren’t any tables in the room.
(lit. ‘In the room there aren’t any tables.’)
or
méi ynu object zài location
!"#$%!"#$%
Méi ynu rén zài fángzi lm.
There are no people in the house.
!"#!$%!"#!$%
Méi ynu zhuszi zài wtzi lm.
There aren’t any tables in the room.
296

Using location as a description |
43.3 |
43.3Using location as a description
Location phrases may also be used to describe a noun. When used as a description, the location phrase precedes the noun, as follows:
Location phrase de noun
the noun at this location [or] the noun in this direction
To help you to understand this structure, the location phrase in each of the following examples is presented in square brackets. Notice that the words ‘that,’ ‘who,’ and ‘which’ that occur in the description in English are not translated into Mandarin. In Mandarin, the noun can be understood as singular or plural.
[ ]= [ ]=
[shpfp shàng] de mpo
the cat [(that is) on the sofa]
[ ]= [ ]=
[fángzi lm] de rén
the person [(who is) in the house]
[ ]= [ ]=
[blibipn] de hú
the lake [(that is) in the north]
[ ]= [ ]=
[zunbian] de rén
the person [(who is) on the left]
The location phrase may itself include a noun with a description:
[ ( ) ]= [ ( ) ]=
[fángzi de hòutou] de rén
the person [(who is) behind the house]
[ ( ) ]= [ ( ) ]=
[túshtgukn (de) duìmiàn] de xuéxiào
the school [(that is) across from the library]
Í9.2, 26.3
Compare the use of the location phrase as a description of a noun, with the use of the location phrase to indicate the location of a noun. Keep in mind that location phrases follow the noun and description phrases precede the noun.
297

EXPRESSING LOCATION AND DISTANCE |
|
43.4 |
Location: noun de location phrase |
Description: location phrase de noun |
|
!" |
!" |
|
!" |
!" |
|
fángzi de hòutou |
hòutou de fángzi |
|
behind the house |
the house that is behind |
|
!" |
!" |
|
fángzi de blimiàn |
blimiàn de fángzi |
|
to the north of the house |
the house to the north |
|
!" |
!" |
|
!" |
!" |
|
háizi de yòubian |
yòubian de háizi |
|
to the right of the child |
the child on the right |
|
! |
! |
|
! |
! |
|
qiántou de rén |
rén de qiántou |
|
the person who is in front |
in front of the person |
|
! |
! |
|
! |
! |
|
sht de shàngtou |
shàngtou de sht |
|
on top of the book |
the book on top |
|
43.4Talking about distance
In Mandarin, distance is always expressed with the word / lí ‘to be separated from.’ All expressions of distance use the following structure. The noun phrases refer to objects or locations.
noun phrase1 / lí noun phrase2 close/far/x distance noun phrase1 is close/far/x distance from noun phrase2
43.4.1Talking about ‘near’ and ‘far’
To say that one object or place is (very) far from another object or place, say:
noun phrase1 / noun phrase2 ( ) / noun phrase1 lí noun phrase2 (hln) yukn
!"#
!"#$%&
Wn jip lí túshtgukn hln yukn.
My house is very far from the library.
To say that one object or place is (very) close to another object or place, say:
noun phrase1 / noun phrase2 ( ) noun phrase1 lí noun phrase2 (hln) jìn
!"( )!"( )
Gsngyuán lí xuéxiào (hln) jìn.
The park is very close to the school.
298

Talking about distance |
43.4 |
To say that an object or place is close to your present location, say:
noun phrase1 / / ( )
noun phrase1 |
lí |
zhèr |
(hln) jìn |
or |
|
|
|
noun phrase1 |
/ / ( ) |
||
noun phrase1 |
lí |
zhèlm |
(hln) jìn |
!"( )!"( )
Gsngyuán lí zhèr (hln) jìn.
The park is (very) close to here.
!"( )!"( )
Xuéxiào lí zhèlm (hln) jìn.
The school is (very) close to here.
To say that an object or place is far from your present location, say:
noun phrase1 / / ( ) /
noun phrase1 |
lí |
zhèr |
(hln) yukn |
or |
|
|
|
noun phrase1 |
/ / ( ) / |
||
noun phrase1 |
lí |
zhèlm |
(hln) yukn |
!"( )!"( )
Gsngyuán lí zhèr (hln) yukn.
The park is (very) far from here.
!"( )!"( )
Xuéxiào lí zhèlm (hln) yukn.
The school is (very) far from here.
Be careful to use / lí ‘to be separated from,’ and not the prepositions dào ‘from’ or / cóng ‘from’ when talking about distance.
Say this |
Not this |
!"#$% |
G !"#$% |
!"#$% |
!"#$% |
Wn jip lí túshtgukn jìn. |
Wn jip dào túshtgukn jìn. |
My house is close to the library. |
|
|
G !"#$% |
|
!"#$% |
|
Wn jip jìn dào túshtgukn. |
43.4.2Talking about specific distance
To indicate the specific distance between two objects or places, say:
noun phrase1 / noun phrase2 ( ) distance noun phrase1 lí noun phrase2 (ynu) distance
299

EXPRESSING LOCATION AND DISTANCE |
43.5 |
!"#( ) ( )!"#( ) ( )
Gsngyuán lí túshtgukn (ynu) spn lm (lù).
The park is three miles from the library.
Commonly used distance words include:
|
lm |
Chinese mile (.5 kilometers) |
|
gsnglm |
kilometer |
|
mm |
meter |
|
Yrng lm |
English mile |
|
lm |
English mile |
43.5Asking about distance
43.5.1Asking about ‘near’ and ‘far’
To ask if an object or place is far from another object or place, say:
noun phrase1 |
|
noun phrase2 |
|
noun phrase1 |
|
noun phrase2 |
|
noun phrase1 |
lí |
noun phrase2 |
yukn ma? |
or |
|
|
|
noun phrase1 |
|
noun phrase2 |
|
noun phrase1 |
|
noun phrase2 |
|
noun phrase1 |
lí |
noun phrase2 |
yukn bù yukn? |
!"#$%&!"#$%&
Nm jip lí túshtgukn yukn ma?
Is your house far from the library?
or
!"#$%$&!"#$%$&
Nm jip lí túshtgukn yukn bù yukn?
Is your house far from the library?
To ask if an object or place is near to another object or place, say:
noun phrase1 |
|
noun phrase2 |
|
noun phrase1 |
|
noun phrase2 |
|
noun phrase1 |
lí |
noun phrase2 |
jìn ma? |
!"#$%&!"#$%&
Nm jip lí túshtgukn jìn ma?
Is your house close to the library?
NOTE As in English, the question ‘is it far?’ is more neutral than the question ‘is it close?’ When the speaker asks ‘is it far?’ he or she typically does not necessarily expect the answer to be ‘far.’ However, when the question is ‘is it close?’ the speaker often expects the answer to be ‘close.’
300

Asking about distance |
43.5 |
To ask if an object or place is far from your present location, say:
!"#$%&!"#$%&
Túshtgukn lí zhèr yukn ma?
Is the library far from here?
or
!"#$%&!"#$%&
Túshtgukn lí zhèlm yukn ma?
Is the library far from here?
Í24.1
43.5.2Asking about specific distances
To ask how far one object or place is from another object or place, say:
!"#$( )!"#$( )
Nm jip lí túshtgukn dus(me) yukn?
How far is your house from the library?
or
!"#$%&'!"#$%&'
Nm jip lí túshtgukn ynu dus yukn?
How far is your house from the library?
Í24.6
301
