
- •Textbook Series
- •Contents
- •1 DC Electrics - Basic Principles
- •Introduction
- •Electromotive Force (EMF)
- •Current
- •Resistance
- •Factors Affecting the Resistance
- •Units of Resistance
- •Resistors
- •Power
- •Series and Parallel Circuits
- •Kirchoff’s Laws
- •Annex A
- •2 DC Electrics - Switches
- •Switches
- •Proximity Detectors
- •Time Switches
- •Centrifugal Switches
- •3 DC Electrics - Circuit Protection and Capacitors
- •Electrical Faults
- •Circuit Protection Devices
- •Fuses
- •The Cartridge Fuse
- •Spare Fuses
- •High Rupture Capacity (HRC) Fuses
- •Dummy Fuses
- •Current Limiters
- •Circuit Breakers
- •Reverse Current Circuit Breakers
- •Capacitors
- •Capacitance
- •Capacitor in a DC Circuit
- •Capacitor in an AC Circuit
- •Capacitors in Parallel
- •Capacitors in Series
- •4 DC Electrics - Batteries
- •Batteries
- •Secondary Cells
- •Lead Acid Battery
- •Alkaline Battery (Nickel Cadmium, NiCad)
- •Battery Checks
- •Battery Charging
- •Secondary Batteries Summary
- •5 DC Electrics - Magnetism
- •Magnetism
- •Temporary Magnets
- •Permanent Magnets
- •Permeability
- •Magnetism
- •The Molecular Structure of Magnets
- •The Magnetic Effect of a Current
- •The Corkscrew Rule
- •The Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
- •The Right Hand Grasp Rule
- •The Strength of the Field of a Solenoid
- •Solenoid and Relay
- •The Forces on a Conductor Which is Carrying a Current
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •6 DC Electrics - Generators and Alternators
- •Electromagnetic Induction
- •Fleming’s Right Hand Rule
- •Faraday’s Law
- •Lenz’s Law
- •Simple Generator
- •Simple DC Generator
- •Characteristics of the Series Wound DC Generator
- •Commutator Ripple
- •Characteristics of the Shunt Wound DC Generator
- •A Compound Wound DC Generator
- •Flashing the Generator Field
- •Alternators
- •Voltage Control
- •Voltage Regulator Operation
- •Layout of a Generator System
- •Load Sharing Circuits
- •Operation of Load Sharing Circuit
- •7 DC Electrics - DC Motors
- •Electric Motors
- •Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
- •Practical DC Motor
- •Back EMF
- •Slow Start Resistor
- •Commutation
- •Series Wound Motors
- •Shunt Wound Motors
- •Starter-generator Systems
- •Actuators
- •Solenoid Actuators
- •Motor Actuator Construction
- •The Split Field Series Actuator
- •The Split Field Series Actuator Operation
- •Motor Actuators
- •Rotary Actuators
- •Linear Actuators
- •Actuator Brakes
- •Actuator Clutches
- •Visual Indicators Used with Linear Actuators
- •Visual Indicators Used with Rotary Actuators
- •Indicator Lights
- •Electromagnetic Indicators
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •8 DC Electrics - Aircraft Electrical Power Systems
- •Aircraft Electrical Power Systems
- •Dipole or Two Wire System
- •Single Pole (Unipole or Earth Return) System
- •Generators and Alternators
- •Voltage Regulators
- •Overvoltage Protection Unit
- •Generator Cut-out or Reverse Current Relay
- •Rectifiers
- •Inverters
- •The Generator Differential Cut-out
- •Generator (or Alternator) Warning Light
- •Generator (or Alternator) Master Switch
- •Monitoring Instruments
- •Ammeters and Voltmeters
- •The Battery
- •Bus Bars
- •Bus Bar Systems
- •Parallel Bus Bar System
- •Load Shedding
- •Generator or Alternator Failure
- •9 DC Electrics - Bonding and Screening
- •Bonding
- •The Static Discharge System or Static Wicks
- •Discharge of Static on Touchdown
- •Screening
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •10 DC Electrics - Specimen Questions
- •Questions – General 1
- •Questions – General 2
- •Answers – General 1
- •Answers – General 2
- •11 AC Electrics - Introduction to AC
- •Introduction
- •The Nature of Alternating Current
- •Terms
- •The Relationship of Current and Voltage in an AC Circuit
- •Resistance in AC Circuits
- •Inductance in AC Circuits
- •Inductive Reactance
- •Capacitance in AC Circuits
- •Capacitive Reactance
- •Impedance
- •Resonant Circuits
- •Summary
- •Power in AC Circuits
- •Power in a Purely Resistive Circuit
- •Power in a Purely Inductive Circuit
- •Power in a Capacitive Circuit
- •Power in a Practical AC Circuit
- •Power Factor
- •Power Factor Resume
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •12 AC Electrics - Alternators
- •Introduction to Aircraft Power Supplies
- •Generators / Alternators
- •Rotating Armature Alternator
- •Rotating Field Alternator
- •Alternator Output Rating
- •A Single Phase Alternator
- •Polyphase Circuits
- •Three Phase Alternator Connections
- •The Four Wire Star Connection
- •Delta Connected Alternator
- •Practical AC Generators
- •Brushed Alternators
- •Brushless Alternators
- •Frequency Wild Alternators
- •Obtaining a Constant Frequency Supply from a Frequency Wild System
- •Constant Frequency Alternators
- •Constant Speed Generator Drive Systems
- •CSDU Fault Indications in the Cockpit
- •The Drive Disconnect Unit (Dog Clutch Disconnect)
- •Variable Speed Constant Frequency Power Systems (VSCF)
- •Self-excited Generators
- •Load Sharing or Paralleling of Constant Frequency Alternators
- •Real Load
- •Reactive Load
- •Parallel Connection
- •Before Connecting in Parallel
- •Layout of a Paralleled System
- •Real Load Sharing
- •Reactive Load Sharing
- •Load Sharing General
- •Alternator Cooling
- •Generator Fault Protection
- •Bus Tie Breakers (BTBs)
- •Discriminatory Circuits
- •Differential Fault Protection
- •Synchronizing Units
- •Generator Failure Warning Light
- •Load Meters
- •Voltage and Frequency Meters
- •Generator Control Unit (GCU)
- •Emergency Supplies
- •The Ram Air Turbine (RAT)
- •The Auxiliary Power Unit (APU)
- •The Static Inverter
- •Ground Power Constant Frequency Supply System
- •Typical Controls and Indications
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •13 AC Electrics - Practical Aircraft Systems
- •Power Distribution
- •The Split Bus System
- •Parallel Bus Bar System
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •14 AC Electrics - Transformers
- •Transformers
- •Transformation Ratio
- •Power in a Transformer
- •Three Phase Transformers
- •Autotransformers
- •Rectification of Alternating Current
- •Half Wave Rectification
- •Full Wave Rectification
- •Three Phase Rectifiers
- •Transformer Rectifier Units (TRUs)
- •Inverters
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •15 AC Electrics - AC Motors
- •Alternating Current Motors
- •The Principle of Operation of AC Motors
- •The Synchronous Motor
- •The Induction Motor
- •The Squirrel Cage Rotor
- •The Induction Motor Stator
- •Slip Speed
- •Starting Single Phase Induction Motors
- •Fault Operation
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •16 AC Electrics - Semiconductors
- •An Introduction to Semiconductors
- •Conductors and Insulators
- •Semiconductors
- •N-Type Material
- •P-Type Material
- •Current Flow
- •The P-N Junction
- •Reverse Bias
- •Forward Bias
- •The Junction Diode
- •The Bipolar or Junction Transistor
- •Summary
- •17 AC Electrics - Logic Gates
- •An Introduction to Logic Gates
- •Binary Logic
- •Truth Tables
- •Gate Symbols
- •Positive and Negative Logic
- •The ‘AND’ Gate
- •The ‘OR’ Gate
- •The ‘INVERT’ or ‘NOT’ Gate
- •The ‘NAND’ Gate
- •The ‘NOR’ Gate
- •The ‘EXCLUSIVE OR’ Gate
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •18 Index

AC Electrics -Transformers 14
Figure 14.3 Autotransformers
Autotransformers are less expensive than two coil transformers because they use less wire; however, they do not electrically isolate the primary and secondary windings and so cannot be used in many circuits for this reason.
Rectification of Alternating Current
A Rectifier is a device which will convert AC into DC. The operation of the Diode Rectifier is described in the Semiconductor chapter, and is a very common device in modern aircraft solid state circuits. It can be used to convert AC to DC or as a “Blocking Diode” (electrical non-return valve) to prevent reverse current flow in a DC system. Some rectifiers are designed to conduct at a predetermined voltage; these rectifiers are called Zener Diodes.
A diode has a high resistance in one direction and a low resistance in the other. The accepted symbol for a diode rectifier and the direction of conventional current flow is shown in
Figure 14.4.
Half Wave Rectification
A diode inserted in the secondary circuit of a transformer will allow current to flow through the load in one direction only. This is termed Half Wave Rectification. The bottom half of the AC waveform is blocked and the frequency of the output is the same as the input, as shown in
Figure 14.4.
Figure 14.4 Single phase half wave rectification
AC Electrics - Transformers 14
233

14 AC Electrics -Transformers
Full Wave Rectification
To fill in the gaps between pulses that have been left from half wave rectification a Bridge Rectifier can be used. As can be seen from Figure 14.5 when one half of the bridge circuit is presenting a high resistance to current flow, the other half is allowing it to flow relatively easily. This arrangement is specifically designed to allow the output of the bridge to be of a single polarity. The output can be smoothed to some extent by the addition of a capacitor placed across it.
Transformers - Electrics AC 14
Figure 14.5 Single phase full wave rectifier
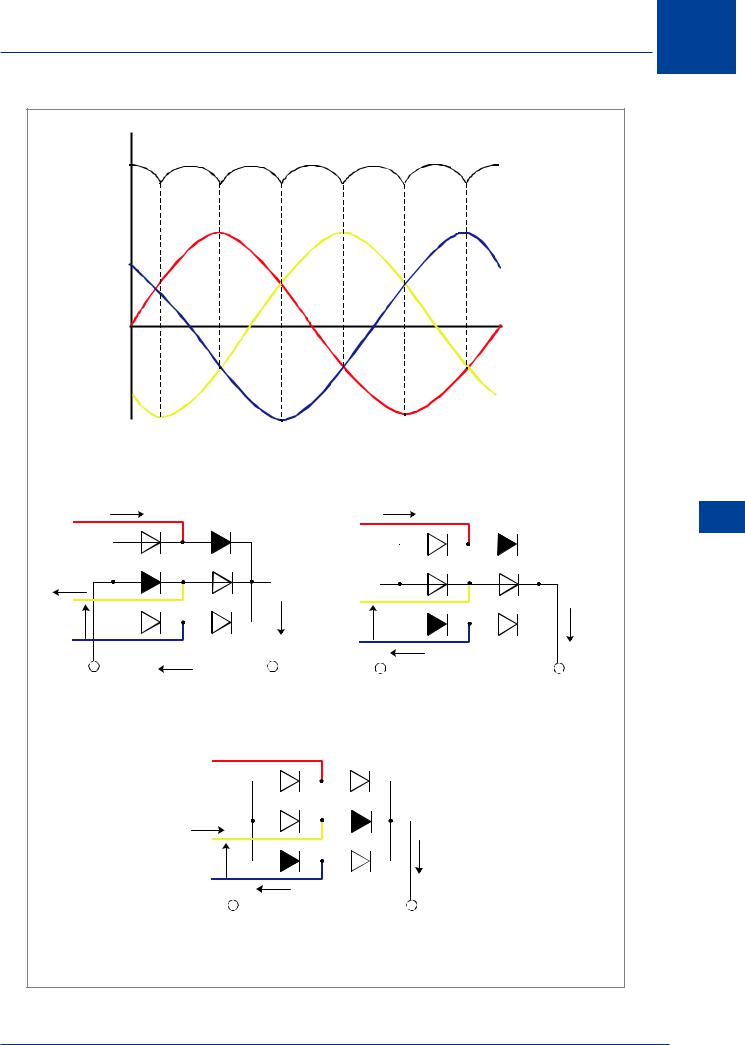
Three Phase Rectifiers
The rectification of a three phase supply can be effected by using a formation of six rectifiers in a bridge circuit.
This is shown in Figure 14.6. The output of a Three Phase Rectifier is essentially a steady output.
234
AC Electrics -Transformers 14
|
|
|
DC OUTPUT |
|
|
|
+ |
PHASE A |
|
PHASE B |
PHASE C |
|
|
|
|||
|
- |
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
A |
14 |
|
|
|
|
||
B |
|
|
|
B |
- Transformers |
|
|
|
Electrics |
||
C |
|
|
|
C |
|
- |
|
|
+ |
- |
AC |
|
DC OUTPUT |
+ |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
LINE VOLTAGE BETWEEN PHASES A AND B |
LINE VOLTAGE BETWEEN PHASES A AND C |
||||
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
+ |
|
|
LINE VOLTAGE BETWEEN PHASES B AND C |
|||
Figure 14.6 Three phase full wave rectifier
235

14 AC Electrics -Transformers
Transformer Rectifier Units (TRUs)
Transformers - Electrics AC 14
TRUs convert AC at one voltage to DC at another voltage by combining the transformer and rectifier in one unit (usually 115 V/ 200 V/ 400 Hz/ 3 phase to 28 V DC) to supply the DC needs of an AC distribution system.
TRUs are invariably multi-phase units to achieve a smooth DC output. Indications of TRU output (amps) can be shown on the main electrical panel on the flight deck.
Cooling is achieved by drawing air through the unit which may be monitored for temperature with an overheat warning supplied.
Inverters
An inverter converts DC to AC.
The inverter in a constant frequency AC equipped aircraft is used as a source of emergency supply if the AC generators fail; then, the inverter is powered by the battery.
Inverters are usually “solid state” static inverters, transistorized in modern aircraft, providing constant frequency AC for operation of flight instruments and other essential AC consumers. Rotary and Static inverters are described in the DC section and are not generally used in modern aircraft.
Aircraft which have a frequency wild distribution system (British Aerospace ATP, ATR 42) use inverters to supply their normal constant frequency requirements. This is done by transforming and rectifying the frequency wild into DC, and then supplying the DC to the inverter (static) to give a controlled AC output.
Inverter output can be monitored for voltage and frequency in the same manner as the main generators.
Cooling is accomplished in the same manner as the TRU.
236
