
experment book
.pdf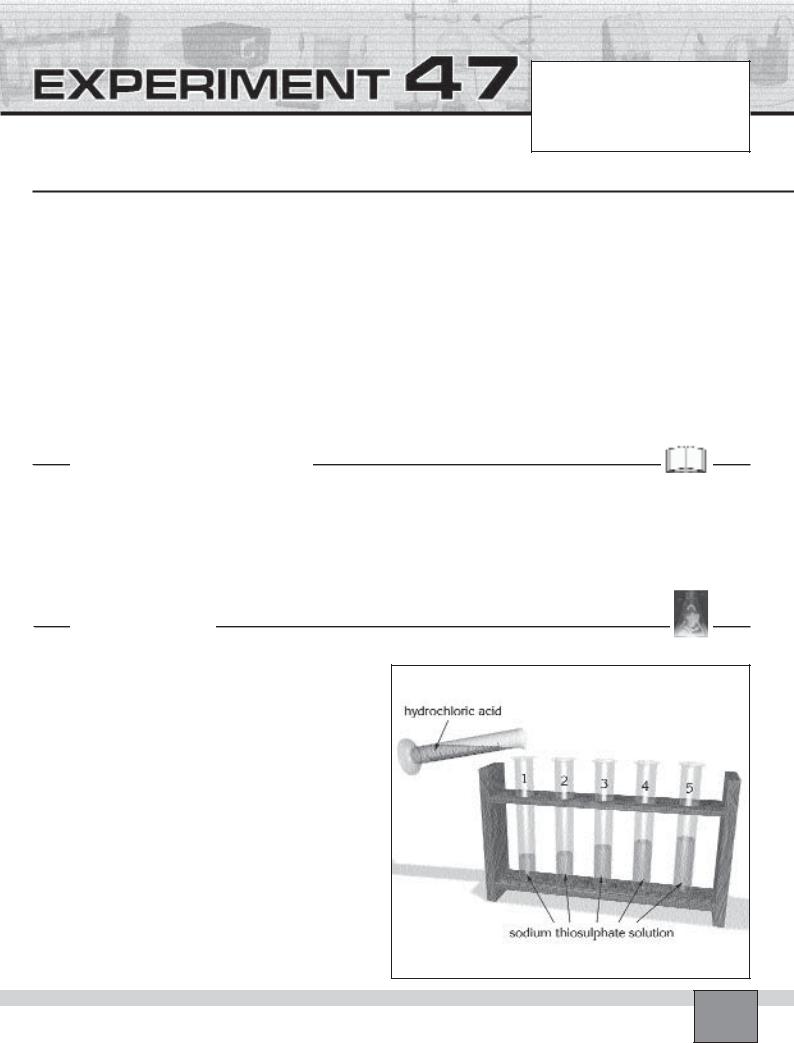
Does the rate of a reaction depend on the concentration?
Date : ...............................................................
Partners : ...............................................................
...............................................................
Grade : ...............................................................
PURPOSE : To observe the effect of the concentration on the rate of the reaction between hydrochloric acid an sodium thiosulpate.
EQUIPMENT and MATERIALS:
Equipment |
|
Chemicals and Other Materials |
• Test tube |
(5) |
• Hydrochloric acid, 2M |
• Graduated cylinder, 10 mL |
(1) |
• Sodium thiosulphate solution, 0.25M |
• Chronometer |
(1) |
• Distilled water |
• Test tube rack |
(1) |
• Label |
|
|
• Sheet of paper |
PRE-LAB DISCUSSION
According to collision theory, a chemical reaction will take place only if the particles of reacting substances are allowed to come into contact. Thus number of collision affects the reaction rate. When the concentration of the reactants is
increased, the number of particles increases. As a result of this, number of collision in a unite time increases. Therefore, the rate of the reaction increases.
PROCEDURE
Set-up |
Figure |
—Place 5 test tubes in the test tube rack and label them from 1 to 5.
—By using graduated cylinder,
—Add 5 mL thiosulphate solution in test tube 1.
—Add 4 mL thiosulphate solution in test tube 2.
—Add 3 mL thiosulphate solution in test tube 3.
—Add 2 mL thiosulphate solution in test tube 4.
—Add 1 mL thiosulphate solution in test tube 5.
—Add 5 mL distilled water into each test tube by using graduated cylinder.
Procedure
1.Measure 2 mL hydrochloric acid in the graduated cylinder.
2.Add the hydrochloric acid into the test tube 1 and at the same time start the chronometer. Record the starting time in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
Experiment – 47 Does the rate of a reaction depend on the concentration? |
123 |
|
3.Shake the test tube 1 once or twice, then place it in the test tube rack.
4.Stop the chronometer when the colour of the solution has just changed. Record the time in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
Note: Take a sheet of paper and draw a cross on it with a marker pen. Hold the paper behind the test tube. Look at the cross
through the solution. Stop the chronometer when the cross disappears. Record the time in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
5.Repeat the steps from 1 to 4 for other solutions in the other four test tubes. Record the measurements in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
OBSERVATIONS AND DATA TABLES 


1.Note your observations in the experiment.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
2.Write the measurements in the experiment.
Time |
|
Test tube 1 |
|
Test tube 2 |
|
Test tube 3 |
|
Test tube 4 |
|
Test tube 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time at initial (ti) |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time at final (tf) |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time interval ( t) |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CALCULATIONS
1.Calculate the concentration of the thiosulphate ion in each diluted solution by using the formula an fill the table below. M1 x V1 = M2 x V2
Test Tubes |
|
|
|
Test tube 2 |
|
|
|
Test tube 4 |
|
Test tube 5 |
|
Test tube 1 |
|
|
Test tube 3 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Concentration of |
|
|
|
M |
|
|
|
M |
|
M |
thiosulphate ion |
|
..................... M |
|
|
..................... M |
|
|
2.Plot concentration of thiosulphate against time and concentration of thiosulphate against 1/time by using time intervals.
Experiment – 47 Does the rate of a reaction depend on the concentration?
124

EVALUATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS 


1.How does the concentration of thiosulphate effect the reaction rate? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
2.What can you deduce from the graphs in the calculation part?
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
3.Does increase in concentration always effect the reaction rate at the same rate? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
4.Does increase in concentration increase the efficiency of a reaction? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
Experiment – 47 Does the rate of a reaction depend on the concentration? |
125 |
|
What is the effect of temperature on reaction rate?
Date : ...............................................................
Partners : ...............................................................
...............................................................
Grade : ...............................................................
PURPOSE : To observe the effect of temperature on the rate of the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulphate.
EQUIPMENT and MATERIALS:
Equipment |
|
• Chronometer |
(1) |
Chemicals and Other Materials |
• Test tube |
(6) |
• Test tube rack |
(1) |
• Hydrochloric acid, 2M |
• Graduated cylinder, 10 mL |
(1) |
• Burner |
(1) |
• Sodium thiosulphate solution, 0.15M |
• Beaker, 250 mL |
(1) |
• Tripod |
(1) |
• Label |
• Thermometer |
(1) |
• Wire gauze |
(1) |
|
PRE-LAB DISCUSSION
It is supposed that chemical reactions occur because, as a first requirement, the atoms, molecules or ions concerned in the reaction collide together. When the temperature of a reaction is increased, heat is supplied to the particles in-
volved in the reaction. This energy increases the speed of particles. As a result, the particles with greater speed collide with one another at more frequent. Therefore, the faster reaction rate is expected.
PROCEDURE
Set-up |
Figure |
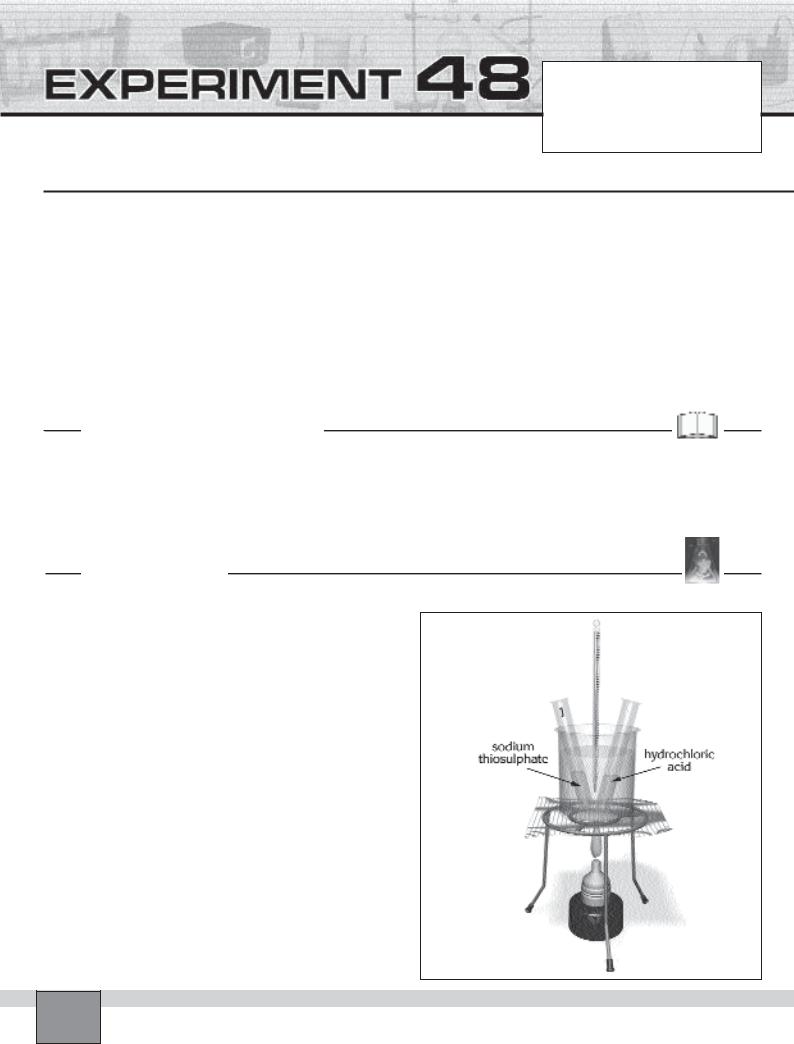
—Place 5 test tubes in the test tube rack and label them from 1 to 5.
—By using graduated cylinder, add 10 mL of thiosulphate solution into the each test tube.
—Fill two third of the 250 mL beaker with tap water. Put the beaker on the tripod as seen in the Figure.
—Take the test tube 1 from the test tube rack and place it into the water in the beaker.
Procedure
1.Measure 2 mL hydrochloric acid with graduated cylinder and pour it into another test tube.
2.Place the test tube in the water in the beaker.
3.Heat the solutions in the beaker by heating the water with burner, until the temperature is 30oC.
4.Stop heating and pour the hydrochloric acid into the test tube 1. At the same time start the chronometer. Record the starting time in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
5.Shake the test tube 1 once or twice, then place it in the beaker.
Experiment – 48 What is the effect of temperature on reaction rate?
126
6.Stop the chronometer when the colour of the solution has just changed. Record the time in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
Note: Take a sheet of paper and draw a cross on it with a marker pen. Hold the paper behind the test tube. Look at the cross through the solution. Stop the chronometer when the cross dis-
appears. Record the time in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
7.Repeat the steps from 1 to 6 for rest of the thiosulphate solutions at 40o, 50o, 60o, 70oC. Record the measurements in Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
OBSERVATIONS AND DATA TABLES 


1.Note your observations in the experiment.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
2.Fill in the blanks in the table with your measurements.
Temperature |
|
Test tube 1 at |
|
Test tube 2 at |
|
Test tube 3 at |
|
Test tube 4 at |
|
Test tube 5 at |
|
30oC |
|
40oC |
|
50oC |
|
60oC |
|
70oC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time at initial (ti) |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time at final (tf) |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
................... sec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time interval ( t) |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
sec |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CALCULATIONS
1.Plot temperature against time and temperature against 1/time.
Experiment – 48 What is the effect of temperature on reaction rate? |
127 |
|

EVALUATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS 


1.How does the temperature affect the reaction rate? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
2.What can you deduce from the graphs in the calculation part?
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
3.Does increase in temperature always increase the reaction rate? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
4.Does increase in temperature affect the efficiency of a reaction? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
Experiment – 48 What is the effect of temperature on reaction rate?
128
How does a catalyst affect the reaction rate?
Date : ...............................................................
Partners : ...............................................................
...............................................................
Grade : ...............................................................
PURPOSE : To examine the effect of catalyst on the rate of reaction.
EQUIPMENT and MATERIALS:
Equipment |
|
Chemicals and Other Materials |
• Test tube |
(3) |
• Hydrochloric acid, 2M |
• Graduated cylinder, 10 mL |
(1) |
• Copper(II) sulphate, 1M |
• Test tube rack |
(1) |
• Copper foil |
|
|
• Granulated zinc |
PRE-LAB DISCUSSION
Catalyst are the substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction. They remain unchanged in amount and in chemical nature at the end of the reaction. But a catalyst may usually increases the rate of a reaction and this is called
positive catalysis. In general, a catalyst will function even though it is present in only minute proportion.
PROCEDURE
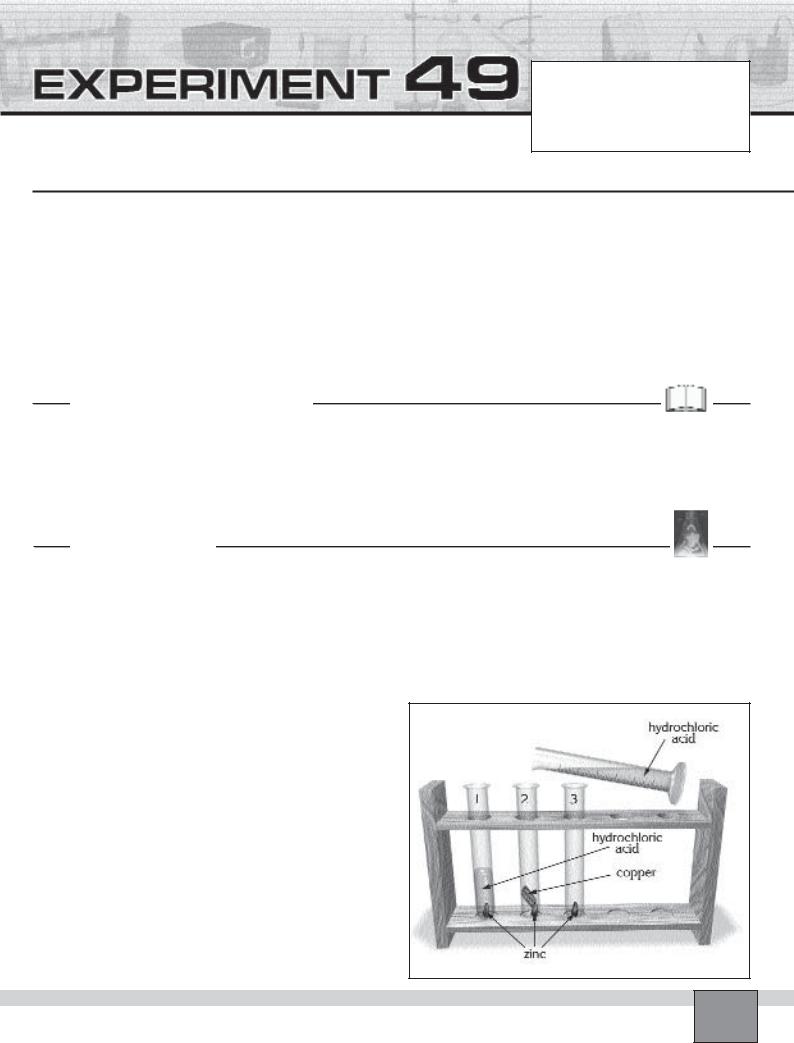
Set-up
—Place 3 test tubes in the test tube rack and label them from 1 to 3.
—Place a two pieces of granulated zinc into the each test tube.
Procedure
1.Measure 5 mL of hydrochloric acid with graduated cylinder and pour it into test tube 1.
Note: Hydrochloric acid is corrosive. Handle with great care.
2.Observe carefully the rate at which hydrogen gas bubbles are formed on the zinc. Note your observation in “Observations and Data Tables”.
3.Place a fine copper foil into the test tube 2 so that it contacts with the granulated zinc.
4.Measure 5 mL of hydrochloric acid with graduated cylinder and pour it into test tube 2.
5.Observe carefully how is the rate of production of hydrogen gas bubbles affected by addition of copper. Note your observation in “Observations and Data Tables”.
6.Measure 5 mL of hydrochloric acid with graduated cylinder and pour it into test tube 3. Observe the rate at which hydrogen gas bubbles are formed on the zinc.
7.Add 1 mL of 1M copper(II) sulphate solution to the mixture and shake the test tube 3. Observe carefully how is the rate of production of hydrogen gas bubbles affected by addition of copper(II) sulphate solution.
8.Note your observations in “Observations and Data Tables”.
Figure
Experiment – 49 How does a catalyst affect the reaction rate? |
129 |
|
OBSERVATIONS AND DATA TABLES 


1.Note your observations on the test tube 1.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
2.Note your observations on the test tube 2.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
3.Note your observations on the test tube 3.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
EVALUATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS 


1.How does a catalyst affect the reaction rate? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
2.List some catalysts that are used in foods and explain their functions in them.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
3.Does addition of catalyst affect the efficiency of a reaction? Explain.
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................................................
Experiment – 49 How does a catalyst affect the reaction rate?
130
How does the addition of a substance disturb an equilibrium reaction?
Date : ...............................................................
Partners : ...............................................................
...............................................................
Grade : ...............................................................
PURPOSE : To study equilibrium systems and their responses to addition of substances according to Le Chatelier’s principle.
EQUIPMENT and MATERIALS:
Part-A
Equipment |
|
Chemicals and Other Materials |
• Beaker, 100 mL |
(1) |
• Iron(III) chloride, 0.1M |
• Test tube |
(5) |
• Potassium tiocyanate, 0.1M |
• Graduated cylinder, 10 mL |
(1) |
• Potassium chloride, 0.1M |
• Test tube rack |
(1) |
• Sodium hydroxide, 0.1M |
• Dropper |
(1) |
• Distilled water |
|
|
• Marker pen |
|
|
|
Part-B |
|
|
Equipment |
|
Chemicals and Other Materials |
• Test tube |
(3) |
• Potassium chromate, 0.1M |
• Graduated cylinder, 10 mL |
(1) |
• Potassium dichromate, 0.1M |
• Test tube rack |
(1) |
• Sodium hydroxide, 1M |
• Dropper |
(1) |
• Hydrogen chloride, 1M |
|
|
• Marker pen |
PRE-LAB DISCUSSION
Some chemical reactions do not go to completion. Rather, the products of these reactions remain in contact with each other and react to reform the original reactants. Such reactions are said to be reversible. In a reversible reaction, the forward reaction and the reverse reaction proceed at the same time. When the rates of the two reactions are equal, a state of chemical equilibrium is said to exist. Under such conditions, both the forward and reverse reactions continue with no net change in the quantities of either products or reactants.
A state of equilibrium is affected by changing concentration, temperature and, if gases are involved, pressure. If a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in one or more of these factors, a stress is placed on the system. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, when a stress is applied to a system
at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in such a way that it tends to minimise the stress. Equilibrium will be re-estab- lished at different point that is, with different concentrations of reactants and products.
In an equilibrium system, there is a simple relationship among the molar concentrations of the reactants and products. To represent this relation we will use the following reaction;
H2(g) + I2(g)  2HI(g)
2HI(g)
Equilibrium expression of the reaction is.
Kc = |
[HI]2 |
|
[H |
] x [I ] |
|
2 |
2 |
|
Experiment – 50 How does the addition of a substance disturb an equilibrium reaction? |
131 |
|

PROCEDURE
Part-A
Set-up
—Place five test tubes in the test tube rack, then number them from 1 to 5 with marker pen.
—Measure 2 mL of 0.1 M FeCl3 solution in the graduated cylinder and pour it into a 100 mL beaker.
—Measure 2 mL of 0.1 M KSCN solution in the graduated cylinder and add it into the same beaker. Shake the beaker to mix the solutions.
—Record the colour of the FeCl3, KSCN and the mixture (FeSCN+2) solutions in the Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
—To dilute the solution, add about 80 mL of distilled water into the beaker to get a light reddish orange colour.
—Place 10 mL of the resultant solution into each test tube by measuring with graduated cylinder.
—Place test tube 1 at one end of the test tube rack to use for colour comparison.
Procedure
1.Add 0.1 M KSCN solution drop by drop with the dropper to the solution in the test tube 2 until a colour change occurs.
2.Add 0.1 M FeCl3 solution drop by drop with the dropper to the solution in the test tube 3 until a colour changes occurs.
Part-B
Set-up
—Number three test tubes from 1 to 3 and place the tubes in the test tube rack.
—Place 5 mL of 0.1 M K2CrO4 solution into the test tubes 1 and 3.
—Place 5 mL of 0.1 M K2Cr2O7 solution into the test tube 2.
—Note the colours of the CrO4-2 ion in the test tube 1 and Cr2O7-2 ion in the test tube 2 in “Observations and Data Tables”.
Procedure
1.Take the test tube 3 and add 1 M HCl drop by drop to the solution until the colour changes. Compare the colour of the solution with the solutions in the test tube 1 and 2. Record your observations in “Observations and Data Tables”.
2.Add 1 M NaOH drop by drop to the same solution in the test tube 3 until the colour change occurs. Compare the colour of the solution with the solutions in the test tube 1 and 2. Record your observations in “Obser-
3.Add 0.1 M KCl solution drop by drop with the dropper to the solution in the test tube 4 until a colour change occurs.
4.Add 0.1 M NaOH solution drop by drop with the dropper to the solution in the test tube 5 until a colour change occurs.
5.Compare the colour of the solutions with the solution in the test tube 1. Record your observations in the Table in “Observations and Data Tables”.
Figure
vations and Data Tables”.
3.Repeat step 1 and 2 one more and record your observations in “Observations and Data Tables”.
Figure
Experiment – 50 How does the addition of a substance disturb an equilibrium reaction?
132
