
- •CONTENTS
- •FIGURES
- •TABLES
- •1.1 Manual Contents
- •1.2 Notational Conventions and Terminology
- •1.3 Related Documents
- •1.4 Application Support Services
- •2.1 Typical Applications
- •2.2 Microcontroller Features
- •2.3 Functional Overview
- •2.3.1 Core
- •2.3.1.3 Register File
- •2.3.2 Memory Controller
- •2.4 Internal Timing
- •2.4.1 Clock and Power Management Logic
- •2.4.2 Internal Timing
- •2.4.2.1 Clock Failure Detection Logic
- •2.4.2.2 External Timing
- •2.4.2.3 Power Management Options
- •2.4.3 Internal Memory
- •2.4.4 Serial Debug Unit
- •2.4.5 Interrupt Service
- •2.5 Internal Peripherals
- •2.5.1 I/O Ports
- •2.5.2 Serial I/O (SIO) Port
- •2.5.3 Synchronous Serial I/O (SSIO) Port
- •2.5.4 Event Processor Array (EPA) and Timer/Counters
- •2.5.7 Stack Overflow Module
- •2.5.8 Watchdog Timer
- •2.6 Special Operating Modes
- •2.7 Chip Configuration Registers
- •3.1 Overview of the Instruction Set
- •3.1.1 BIT Operands
- •3.1.2 BYTE Operands
- •3.1.4 WORD Operands
- •3.1.5 INTEGER Operands
- •3.1.9 Converting Operands
- •3.1.10 Conditional Jumps
- •3.1.11 Floating-Point Operations
- •3.1.12 Extended Instructions
- •3.2 Addressing Modes
- •3.2.1 Direct Addressing
- •3.2.2 Immediate Addressing
- •3.2.3 Indirect Addressing
- •3.2.3.1 Extended Indirect Addressing
- •3.2.3.2 Indirect Addressing with Autoincrement
- •3.2.3.3 Extended Indirect Addressing with Autoincrement
- •3.2.3.4 Indirect Addressing with the Stack Pointer
- •3.2.4 Indexed Addressing
- •3.2.4.3 Extended Indexed Addressing
- •3.2.4.4 Zero-indexed Addressing
- •3.3 Considerations for Crossing Page Boundaries
- •3.4 Software Protection Features and Guidelines
- •4.1 Memory Map Overview
- •4.2 Memory Partitions
- •4.2.1 External Memory
- •4.2.2 Internal ROM
- •4.2.2.1 Program Memory in Page FFH
- •4.2.2.3 Reserved Memory Locations
- •4.2.2.4 Interrupt, PIH, and PTS Vectors
- •4.2.2.5 Chip Configuration Bytes
- •4.2.3 Internal RAM (Code RAM)
- •4.2.4.2 Peripheral SFRs
- •4.2.5 Register File
- •4.2.5.2 Stack Pointer (SP)
- •4.3 Windowing
- •4.3.1 Selecting a Window
- •4.3.2 Addressing a Location Through a Window
- •4.3.2.4 Unsupported Locations Windowing Example
- •4.3.2.5 Using the Linker Locator to Set Up a Window
- •4.3.3 Windowing and Addressing Modes
- •4.4 Controlling Read Access to the Internal ROM
- •4.5 Remapping Internal ROM
- •5.1 Functional Overview
- •5.2 Stack Operations
- •5.3 Stack Overflow Module Registers
- •5.4 Programming the Stack Overflow Module
- •5.4.1 Initializing the Stack Pointer
- •5.4.2 Enabling the Stack Overflow Module and Specifying Stack Boundaries
- •6.1 Overview of the Interrupt Control Circuitry
- •6.2 Interrupt Signals and Registers
- •6.3 Interrupt Sources, Priorities, and Vector Addresses
- •6.3.1 PIH Interrupt Sources, Priorities, and Vector Addresses
- •6.3.1.1 Using Software to Provide the Vector Address
- •6.3.1.2 Providing the Vector Address in Response to a CPU Request
- •6.3.2 Special Interrupts
- •6.3.2.1 Unimplemented Opcode
- •6.3.2.2 Software Trap
- •6.3.2.4 Stack Overflow
- •6.3.3 External Interrupt Signal
- •6.3.4 Shared Interrupt Requests
- •6.4 Interrupt Latency
- •6.4.1 Situations that Increase Interrupt Latency
- •6.4.2 Calculating Latency
- •6.4.2.2 PTS Interrupt Latency
- •6.5 Programming the Interrupts
- •6.5.1 Modifying Interrupt Priorities
- •6.5.2 Determining the Source of an Interrupt
- •6.6 Initializing the PTS Control Blocks
- •6.6.1 Specifying the PTS Count
- •6.6.2 Selecting the PTS Mode
- •6.6.3 Single Transfer Mode
- •6.6.4 Block Transfer Mode
- •6.6.5 Dummy Mode
- •7.1 I/O Ports Overview
- •7.2 Configuring the Port Pins
- •7.2.2 Configuring Ports 3 and 4 (Address/Data Bus)
- •7.2.3 Port Configuration Example
- •7.3.1 Address and Data Signals (Ports 3, 4, and EPORT)
- •7.3.1.1 EPORT Status During Reset, CCB Fetch, Idle, Powerdown, and Hold
- •7.3.5 External Interrupt Signal (Port 2)
- •7.3.6 PWM Signals (Port 11)
- •7.3.7 Serial I/O Port Signals (Ports 2 and 7)
- •7.3.8 Special Operating Mode Signal (Port 5 Pin 7)
- •7.3.9 Synchronous Serial I/O Port Signals (Port 10)
- •7.4 I/O Port Internal Structures
- •7.4.3 Internal Structure for Ports 3 and 4 (Address/Data Bus)
- •8.1 Serial I/O (SIO) Port Functional Overview
- •8.2 Serial I/O Port Signals and Registers
- •8.3 Serial Port Modes
- •8.3.1 Synchronous Mode (Mode 0)
- •8.3.2 Asynchronous Modes (Modes 1, 2, and 3)
- •8.3.2.1 Mode 1
- •8.3.2.2 Mode 2
- •8.3.2.3 Mode 3
- •8.3.2.4 Multiprocessor Communications
- •8.4 Programming the Serial Port
- •8.4.1 Configuring the Serial Port Pins
- •8.4.2 Programming the Control Register
- •8.4.3 Programming the Baud Rate and Clock Source
- •8.4.4 Enabling the Serial Port Interrupts
- •8.4.5 Determining Serial Port Status
- •CHAPTER 9 Synchronous Serial I/O (SSIO) Port
- •9.1 SSIO Port Overview
- •9.1.1 Standard Mode
- •9.1.2 Duplex Mode
- •9.2 SSIO pORT sIGNALS AND rEGISTERS
- •9.3 ssio Port Operation
- •9.3.1 Transmitting and Receiving Data
- •9.3.1.1 Normal Transfers (All Modes)
- •9.3.1.2 Handshaking Transfers (Standard Mode Only)
- •9.4 Programming the SSIO Port
- •9.4.1 Configuring the SSIO Port Pins
- •9.4.2 Configuring the SSIO Registers
- •9.4.2.1 The SSIO Baud (SSIO_BAUD) Register
- •9.4.2.3 The SSIO 0 Clock (SSIO0_CLK) Register
- •9.4.2.4 The SSIO 1 Clock (SSIO1_CLK) Register
- •9.4.3 Enabling the SSIO Interrupts
- •9.5 Programming Considerations
- •9.5.2 Standard Mode Considerations
- •9.5.3 Duplex Mode Considerations
- •10.1 PWM FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
- •10.2 PWM Signals and Registers
- •10.3 pwm operation
- •10.4 Programming the Frequency and Period
- •10.5 Programming the Duty Cycle
- •10.5.1 Sample Calculations
- •10.5.2 Reading the Current Value of the Down-counter
- •10.5.3 Enabling the PWM Outputs
- •10.5.4 Generating Analog Outputs
- •11.1 EPA Functional Overview
- •11.2 EPA and Timer/Counter Signals and Registers
- •11.3 Timer/Counter Functional Overview
- •11.3.1 Timer Multiplexing on the Time Bus
- •11.4 EPA Channel Functional Overview
- •11.4.1 Operating in Input Capture Mode
- •11.4.2 Operating in Output Compare Mode
- •11.4.3 Operating in Compare Mode with the Output/Simulcapture Channels
- •11.4.4 Generating a 32-bit Time Value
- •11.4.5 Controlling a Pair of Adjacent Pins
- •11.5 Programming the EPA and Timer/Counters
- •11.5.1 Configuring the EPA and Timer/Counter Signals
- •11.5.2 Programming the Timers
- •11.5.3 Programming the Capture/Compare Channels
- •11.5.4 Programming the Compare-only (Output/Simulcapture) Channels
- •11.6 Enabling the EPA Interrupts
- •11.7 Determining Event Status
- •CHAPTER 12 Analog-to-digital (A/D) Converter
- •12.1 A/D Converter Functional Overview
- •12.2 A/D Converter Signals and Registers
- •12.3 A/D Converter Operation
- •12.4 Programming the A/D Converter
- •12.4.1 Programming the A/D Test Register
- •12.4.2 Programming the A/D Result Register (for Threshold Detection Only)
- •12.4.3 Programming the A/D Time Register
- •12.4.4 Programming the A/D Command Register
- •12.4.5 Programming the A/D Scan Register
- •12.4.6 Enabling the A/D Interrupt
- •12.5 Determining A/D Status and Conversion Results
- •12.6 Design Considerations
- •12.6.1 Designing External Interface Circuitry
- •12.6.1.1 Minimizing the Effect of High Input Source Resistance
- •12.6.1.2 Suggested A/D Input Circuit
- •12.6.1.3 Analog Ground and Reference Voltages
- •12.6.2 Understanding A/D Conversion Errors
- •CHAPTER 13 Minimum Hardware Considerations
- •13.1 Minimum Connections
- •13.1.1 Unused Inputs
- •13.1.2 I/O Port Pin Connections
- •13.2 Applying and Removing Power
- •13.3 Noise Protection Tips
- •13.4 The On-chip Oscillator Circuitry
- •13.5 Using an External Clock Source
- •13.6 Resetting the Microcontroller
- •13.6.1 Generating an External Reset
- •13.6.2 Issuing the Reset (RST) Instruction
- •13.6.3 Issuing an Illegal IDLPD Key Operand
- •13.6.4 Enabling the Watchdog Timer
- •13.6.5 Detecting Clock Failure
- •13.7 Identifying the Reset Source
- •14.1 Special Operating Mode Signals and Registers
- •14.2 Reducing Power Consumption
- •14.3 Idle Mode
- •14.3.1 Enabling and Disabling Idle Mode
- •14.3.2 Entering and Exiting Idle Mode
- •14.4 Powerdown Mode
- •14.4.1 Enabling and Disabling Powerdown Mode
- •14.4.2 Entering Powerdown Mode
- •14.4.3 Exiting Powerdown Mode
- •14.4.3.1 Generating a Hardware Reset
- •14.4.3.2 Asserting the External Interrupt Signal
- •14.4.3.3 Selecting an External Capacitor
- •14.5 ONCE Mode
- •CHAPTER 15 Interfacing with External Memory
- •15.1 Internal and External Addresses
- •15.2 External Memory Interface Signals and Registers
- •15.3 The Chip-select Unit
- •15.3.1 Defining Chip-select Address Ranges
- •15.3.2 Controlling Bus Parameters
- •15.3.3 Chip-select Unit Initial Conditions
- •15.3.4 Programming the Chip-select Registers
- •15.3.5 Example of a Chip-select Setup
- •15.4 Chip Configuration Registers and Chip Configuration Bytes
- •15.5 Bus Width and Multiplexing
- •15.5.1 A 16-bit Example System
- •15.5.2 16-bit Bus Timings
- •15.5.3 8-bit Bus Timings
- •15.5.4 Comparison of Multiplexed and Demultiplexed Buses
- •15.6 Wait States (Ready Control)
- •15.7 Bus-hold Protocol
- •15.7.1 Enabling the Bus-hold Protocol
- •15.7.2 Disabling the Bus-hold Protocol
- •15.7.3 Hold Latency
- •15.7.4 Regaining Bus Control
- •15.8 Write-control Modes
- •15.9 System Bus AC Timing Specifications
- •15.9.1 Deferred Bus-cycle Mode
- •15.9.2 Explanation of AC Symbols
- •15.9.3 AC Timing Definitions
- •16.1 Serial Debug Unit (SDU) Functional Overview
- •16.2 SDU Signals and Registers
- •16.3 SDU Operation
- •16.3.1 SDU State Machine
- •16.3.2 Code RAM Access State Machine
- •16.3.3 Minimizing Latency
- •16.4 Code RAM Access
- •16.4.1 Code RAM Data Transfer
- •16.4.2 Code RAM Access Instructions
- •16.4.3 Code RAM Data Transfer Example
- •16.5 SDU Interface Connector
- •17.1 Signals and Registers
- •17.2 Memory Protection Options
- •17.3 Entering Test-ROM Routines
- •17.3.1 Power-up and Power-down Sequences
- •17.4 ROM-dump Routine and Circuit
- •17.5 Serial Port Mode Routine
- •17.5.1 Serial Port RISM
- •17.5.2 Serial Port Mode Circuit
- •17.6 SDU RISM Execution Routine
- •17.6.1 SDU RISM Data Transfer
- •17.6.1.1 SDU RISM Data Transfer Before
- •17.6.1.2 SDU RISM Data Transfer After
- •17.6.2 SDU RISM Execution Circuit
- •17.7 RISM Command Descriptions
- •17.8 Executing Programs from Register RAM
- •17.9 RISM Command Examples
- •17.9.1 Serial Port Mode RISM Read Command Example
- •17.9.2 Serial Port Mode RISM Write Command Example
- •17.9.3 SDU RISM Execution Write Command Example
- •17.9.4 SDU RISM Execution Go Command Example
- •B.1 Functional Groupings of Signals
- •B.2 Signal Descriptions
- •B.3 Default Conditions
8XC196EA USER’S MANUAL
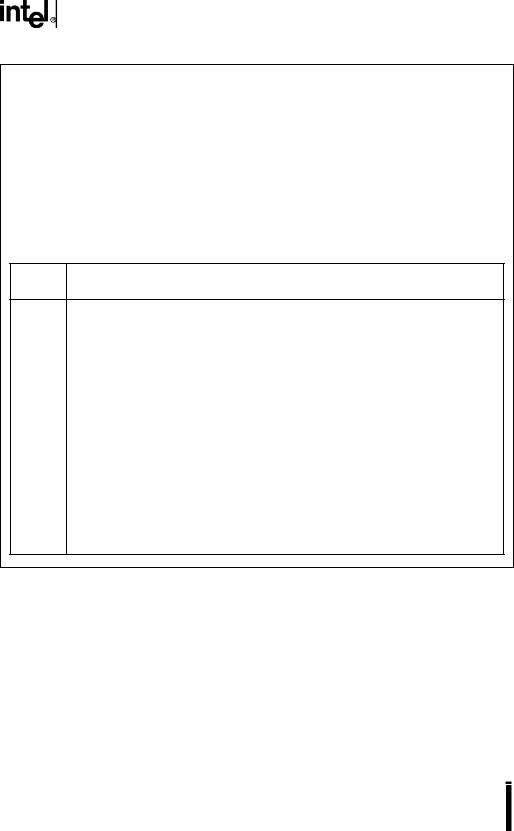
PIH1_PTSSRV |
Address: |
1EA4H |
|
Reset State: |
0000H |
The PTS service (PIH1_PTSSRV) register for peripheral interrupt handler 1 is used by the hardware to indicate that the final PTS interrupt has been serviced by the PTS routine. When PTSCOUNT reaches zero, hardware clears the corresponding PIH1_PTSSEL bit and sets the PIH1_PTSSRV bit, which requests the end-of-PTS interrupt. When the end-of-PTS interrupt is called, hardware clears the PIH1_PTSSRV bit. The end-of-PTS interrupt service routine must set the PIH1_PTSSEL bit to reenable the PTS channel.
15
EPA16 |
OS7 |
OS6 |
OS5 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OS0 |
OVRTM1 |
OVRTM2 |
OVRTM3 |
|
|
|
|
8
OS4 |
OS3 |
OS2 |
OS1 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
OVRTM4 |
OVR0 |
OVR1 |
OVR2 |
|
|
|
|
Bit
Function
Number
15:0 A bit is set by hardware to request an end-of-PTS interrupt for the corresponding interrupt through its standard interrupt vector.
The standard interrupt vector locations are as follows:
Bit Mnemonic |
Interrupt |
Standard Vector |
EPA16 |
EPA Capture/Compare Channel 16 |
FF213CH |
OS7 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 7 |
FF2138H |
OS6 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 6 |
FF2134H |
OS5 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 5 |
FF2130H |
OS4 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 4 |
FF212CH |
OS3 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 3 |
FF2128H |
OS2 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 2 |
FF2124H |
OS1 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 1 |
FF2120H |
OS0 |
Output Simulcapture Channel 0 |
FF211CH |
OVRTM1 |
Timer 1 Overflow/Underflow |
FF2118H |
OVRTM2 |
Timer 2 Overflow/Underflow |
FF2114H |
OVRTM3 |
Timer 3 Overflow/Underflow |
FF2110H |
OVRTM4 |
Timer 4 Overflow/Underflow |
FF210CH |
OVR0 |
EPA Channel 0 Capture Overrun |
FF2108H |
OVR1 |
EPA Channel 1 Capture Overrun |
FF2104H |
OVR2 |
EPA Channel 2 Capture Overrun |
FF2100H |
Figure 6-22. PIH1 PTS Service (PIH1_PTSSRV) Register
6.6.2Selecting the PTS Mode
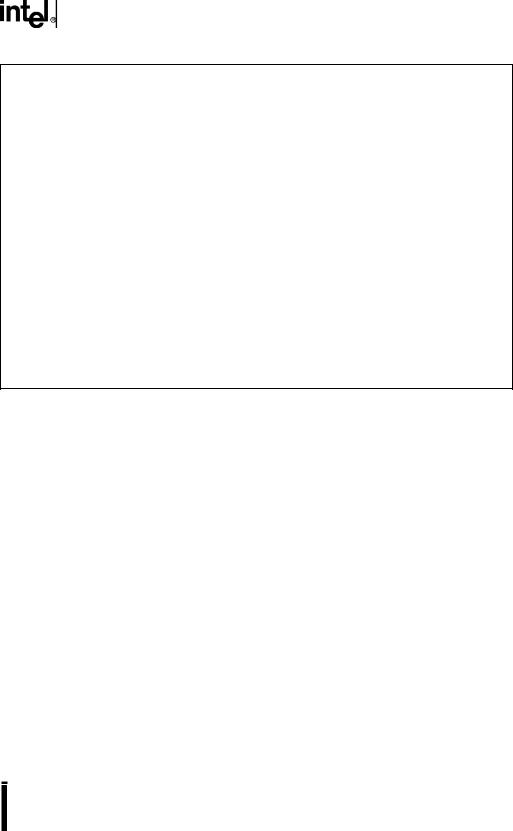
The second byte of each PTSCB is always an 8-bit value called PTSCON. Bits 5–7 select the PTS mode (Figure 6-23). The function of bits 0–4 differ for each PTS mode. Refer to the sections that describe each mode in detail to see the function of these bits. Table 6-6 on page 6-18 lists the cycle execution times for each PTS mode.
6-34
STANDARD AND PTS INTERRUPTS
PTSCON |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address: PTSCB + 1 |
||
The PTS control (PTSCON) register selects the PTS mode and sets up control functions for that |
|||||||||||||
mode. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M2 |
M1 |
|
M0 |
|
|
† |
|
|
† |
† |
|
† |
† |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bit |
Bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|
|
||
Number |
Mnemonic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7:5 |
M2:0 |
PTS Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
These bits select the PTS mode: |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
M2 |
M1 |
M0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
dummy mode |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
block transfer |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
reserved |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
reserved |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
reserved |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
single transfer |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
missed-event |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
reserved |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
† The function of this bit depends upon which mode is selected. See the PTS control block description in each PTS mode section.
Figure 6-23. PTS Mode Selection Bits (PTSCON Bits 7:5)
6.6.3Single Transfer Mode
In single transfer mode, an interrupt causes the PTS to transfer a single byte or word (selected by the BW bit in PTSCON) from one memory location to another. This mode is typically used with serial I/O or synchronous serial I/O interrupts. It can also be used with the EPA to move captured time values from the event-time register to internal RAM for further processing. See AP-445, 8XC196KR Peripherals: A User’s Point of View , for application examples with code. Figure 6-24 shows the PTS control block for single transfer mode.
6-35

8XC196EA USER’S MANUAL
PTS Single Transfer Mode Control Block
In single transfer mode, the PTS control block contains both a source and a destination address (PTSSRC and PTSDST), a control register (PTSCON), and a transfer count (PTSCOUNT).
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
Unused |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
Unused |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PTSDST (H) |
|
|
|
PTS Destination Address (high byte) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PTSDST (L) |
|
|
|
PTS Destination Address (low byte) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PTSSRC (H) |
|
|
|
|
PTS Source Address (high byte) |
|
|
|||||
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
PTSSRC (L) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PTS Source Address (low byte) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PTSCON |
|
M2 |
M1 |
M0 |
|
BW |
|
SU |
DU |
|
SI |
DI |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PTSCOUNT |
|
|
|
Consecutive Byte or Word Transfers |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
Location |
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
PTSDST |
PTSCB + 4 |
PTS Destination Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Write the destination memory location to this register. A valid address is |
|||||||||
|
|
|
any unreserved memory location within page 00H; however, it must |
|||||||||
|
|
|
point to an even address if word transfers are selected. |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
PTSSRC |
PTSCB + 2 |
PTS Source Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Write the source memory location to this register. A valid address is any |
|||||||||
|
|
|
unreserved memory location within page 00H; however, it must point to |
|||||||||
|
|
|
an even address if word transfers are selected. |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 6-24. PTS Control Block — Single Transfer Mode
6-36

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STANDARD AND PTS INTERRUPTS |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
PTS Single Transfer Mode Control Block (Continued) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
Location |
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
PTSCON |
PTSCB + 1 |
PTS Control Bits |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
M2:0 |
PTS Mode |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
M2 |
M1 |
M0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
single transfer mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
BW |
Byte/Word Transfer |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
0 |
= word transfer |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
1 |
= byte transfer |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
SU† |
Update PTSSRC |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
0 |
= |
reload original PTS source address after each byte or word |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
transfer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
= |
retain current PTS source address after each byte or word |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
transfer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
DU† |
Update PTSDST |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
0 |
= |
reload original PTS destination address after each byte or |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
word transfer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
= |
retain current PTS destination address after each byte or |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
word transfer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
SI† |
PTSSRC Autoincrement |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
0 |
= |
the contents of PTSSRC are not incremented after each |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
byte or word transfer |
|
||
|
|
|
|
1 |
= |
the contents of PTSSRC are incremented after each byte |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
or word transfer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
DI† |
PTSDST Autoincrement |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
0 |
= |
the contents of PTSDST are not incremented after each |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
byte or word transfer |
|
||
|
|
|
|
1 |
= |
the contents of PTSDST are incremented after each byte or |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
word transfer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
PTSCOUNT |
PTSCB + 0 |
Consecutive Word or Byte Transfers |
|
|||||
|
|
|
Defines the number of words or bytes that will be transferred during the |
|
|||||
|
|
|
single transfer routine. Each word or byte transfer is one PTS cycle. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
Maximum value is 255. |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
†The DU/DI bits and SU/SI bits are paired in single transfer mode. Each pair must be set or cleared together. However, the two pairs, DU/DI and SU/SI, do not need to be equal.
Figure 6-24. PTS Control Block — Single Transfer Mode (Continued)
The PTSCB in Table 6-8 defines nine PTS cycles. Each cycle moves a single word from location 20H to an external memory location. The PTS transfers the first word to location 6000H. Then it increments and updates the destination address and decrements the PTSCOUNT register; it does not increment the source address. When the second cycle begins, the PTS moves a second word from location 20H to location 6002H. When PTSCOUNT equals zero, the PTS will have filled locations 6000–600FH, and an end-of-PTS interrupt is generated.
6-37
