
- •1. Вступ
- •2. Звуки і букви
- •3. Алфавіт
- •4. Транскрипція
- •5. Класифікація звуків
- •6. Інтонація
- •7. Наголос
- •8. Типи складів
- •9. Характеристика звуків
- •Голосні звуки
- •Дифтонги
- •10. Читання буквосполучень
- •11. "Німі" літери
- •12. Органи мовлення
- •Заняття 1 (lesson one)
- •III. Speaking: About Myself
- •Personal Information Sheet
- •About My Family and Myself
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •1. Наголошений склад:
- •2. Ненаголошений склад: а [з] - aside [a'said], data ['deita] ai, ay [ei] - play, rain, nail ei, ey [ei] - vein, fey еа [I:] - peace, seat, tea name, pain, may
- •II. Читання приголосних звуків
- •Exercise 13. Прочитайте cj
- •III. Speaking: Elements of Conversation
- •Exercise 2. Вивчіть наступні вирази
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •V. Independent Work: Introducing People
- •Introducing People
- •/ Study at the Medical College
- •III. Grammar Exercises
- •IV. Independent Work: My Medical College
- •[Зо] [d]
- •II. Speaking: My Future Profession
- •III. Grammar Exercises
- •IV. Independent Work: Where Do Nurses Work?
- •Where Do Nurses Work?
- •1. Відкритий склад
- •II. Speaking: Nurse's Working Day
- •In a Hospital
- •III. Grammar Exercises
- •IV. Independent Work: Florence Nightingale
- •Igh - [аі]
- •II. Speaking: English for Modern Medical Specialists
- •/ Study English
- •IV. Independent Work: English as Means of International Communication
- •English as Means of International Communication
- •I. Speaking
- •We Study Anatomy
- •In class:
- •III. Independent Work: From the History of Anatomy
- •Some Notes from the History of Anatomy and Physiology
- •I. Speaking: Skeleton
- •Skeleton
- •III. Independent Work: Indoor Activities or Home Interests
- •I. Speaking: Internal Organs
- •Internal Organs
- •II. Independent Work: Body Systems
- •Body Systems
- •I. Speaking: Heart
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •It is early. - Рано. It is late. - Пізно. It is time. - Пора. It is high time. - Давно пора.
- •It's morning. - Ранок. It's evening. - Вечір. It's night. - Ніч. It's afternoon. - Полудень.
- •I. Speaking: How to Take a Pulse
- •Heart (Part 2)
- •How the Second Hand in Your Watch Was Invented
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: My Heart Will Go on
- •My Heart Will Go on
- •I. Speaking: Blood
- •Heart and Blood
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Functions of Blood
- •Functions of Blood
- •I. Speaking: Blood Pressure
- •Blood Pressure
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Instant Blood Test
- •Instant Blood Test
- •I. Speaking: Healthy Way of Life
- •Exercise 6. Match the words/word combinations.
- •Eternal Youth Laws
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Are You Going to Live to 100?
- •I. Speaking: Vitamins
- •Vitamins
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: What You Should Know about Vitamins
- •Vitamins: Their Uses
- •Vitamins: Six Cooking Tips
- •I. Control Test Variant 1
- •Variant 2
- •II. Grammar
- •Exercise 5. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian. Mind the meaning of one.
- •I. Speaking: First Medical Aid (Part I)
- •First Aid
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •Ill. Independent Work: The Strange Doctor
- •The Strange Doctor
- •I. Speaking: First Medical Aid (Part II)
- •Text 1 Bruises
- •Text 2 Burns
- •Text 4 Spinal Injuries
- •Text 5 Unconsciousness
- •Text б Cuts, Bleeding
- •II. Independent Work: Future Tense
- •Lessons nineteen-twenty
- •І. Texts for Home Reading Text a Early Folk Medicine
- •Text в Higher Education in Ukraine
- •Text c English Universities and Colleges
- •I. Speaking: Diseases. Symptoms
- •When We Have Pain
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: From the History of Medicine
- •I. Speaking: Things for Nursing
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •In question - який вивчається; який обговорюється; який викликає сумнів; спірний under study - який вивчається under discussion - який обговорюється
- •III. Independent Work: Medicine
- •Medicine
- •I. Speaking: When I'm III
- •The Doctor
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Health
- •I. Speaking: a Visit to a Doctor
- •At the Doctor's
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •Hi. Independent Work: Cold War
- •Cold War
- •I. Speaking: Illness
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Why Are British Sailors Called "Limeys"?
- •Why Are British Sailors Called "Limeys"?
- •6. What are some foods that you should eat so that you get enough vitamin c?
- •I. Speaking: Infectious Diseases
- •Infectious Diseases
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Bacteria
- •Bacteria
- •I. Speaking: Children Diseases
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •Rickets
- •I. Speaking: Surgical Department
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Superlatives
- •Superlatives
- •I. Speaking: Operating Nurse
- •Operation
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Surgery
- •Surgery
- •Introduction
- •I. Speaking: Work of a Laboratory Assistant
- •Work of a Laboratory Assistant
- •Pain in the Leg
- •Your Arm Is out of Joint
- •Leg Fracture
- •A Dog Bit Me
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Speaking: Teeth
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: What Happens to a Hamburger
- •What Happens to a Hamburger
- •I. Speaking: At the Dentist's. Dental Instruments
- •II. You are examining your patient's oral cavity. Ask the patient to perform thefollowing.
- •Dental Calculus
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: What Happens to a Hamburger What Happens to a Hamburger
- •I. Speaking: Medicines and Their Forms
- •At the Chemist's
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: d.I. Mendeleev
- •Outstanding Russian Chemist d.I. Mendeleev
- •I. Speaking: Chemical Elements. Properties of Substances
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Chemical Elements of Living Matter
- •Chemical Elements of Living Matter
- •I. Speaking: At the Chemist's
- •At the Chemist's
- •At the Chemist's
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Aspirin
- •Ordinary Aspirin Is Truly a Wonder Drug
- •I. Speaking: Obstetrics and Gynecology
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Childbirth
- •I. Speaking
- •Computers in Our Life
- •Interpreter: ...
- •Interpreter: ....
- •Interpreter: ....
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Control Test
- •Medicinal Plants
- •X All child's diseases are caused by
- •Independent Reading
- •/. Health Service in Ukraine
- •2. Doctors and Patients
- •3. Medicine and Health Care
- •Physicians
- •4. Computers Concern You
- •5. Hobbies and Leisure Time Occupations
- •Outdoor Activities or Activities outside the Home
- •6. Are You Left-Handed?
- •7. Vegetarians
- •I. Speaking: Human Body
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Speaking: Chemistry, Matter and Life
- •Chemistry, Matter, and Life
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Speaking: Cells and Their Functions
- •Cells and Their Functions
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Speaking: Tissues, Glands and Membranes
- •Voluntary ['vubntsri] довільний
- •Visceral ['visarsl] що стосується нутрощів
- •II. Independent Work: Diseases
- •Study of Diseases
- •I. Speaking: Skeleton
- •Exercise 1. Read and learn the following words, remember their Latin or Greek equivalents.
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •IhaL cresl
- •I want I'd like He agreed The wounded asked She likes You can Exercise 2. Make up sentences, translate them. Name the forms of the infinitive.
- •111. Independent Work: Spinal Curves
- •Spinal Curves
- •I. Speaking: Bones
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Traumatological Case Report
- •Traumatological Case Report
- •I. Speaking: Joints
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
- •Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
- •Exercise 2. Make up a dialog: you are a traumatologist and you receive a patient with severe pain in his knee.
- •I. Speaking: Musculoskeletal System
- •Musculoskeletal System
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Muscle Tissues
- •I. Speaking: Skin (Integumentary System)
- •Is eczema a contagious disease?
- •9) What is urticaria?
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •It is not difficult for the doctor to treat the disease.
- •10) What clotting disorders do you know?
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •1.1 Can't hear a word, though he seems to be speaking. 2.1 am happy not to have failed you.
- •It is not so difficult for him to diagnose this disease.
- •III. Independent Work: Blood Tests
- •7. Bone marrow biopsy gives valuable information to diagnose bone marrow disorders,cukemia and anemia.
- •1. The most numerous cells of blood are ...
- •Interspace [,ints'speis] проміжок; інтервал
- •In the left chamber the atrium and ventricle are separated by the mitral valve. In the rig: chamber the atrium and ventricle are separated by the tricuspid valve.
- •1. Endocarditis [,endsuka:'daitis] means "inflammation of the lining of the heart cavities"but it most commonly refers to valvular disease.
- •3. Pericarditis [,peri:ka:'daitis] refers to disease of the serous membrane on the heartsurface, as well as that lining the pericardial sac.
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Heart Sounds
- •Visceral ['visaral] що стосується нутрощів
- •Vary ['veari] мінятись; змінюватись
- •III. Independent Work: Cardiovascular Diseases
- •1) To be of great importance; at present; scientists consider; cardiovascular diseases;
- •In the treatment of some cardiovascular diseases; to have been achieved; definite success.
- •I. Speaking: Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Tissue
- •Inguinal [irjgwm(a)l] пахвинний
- •Vessels in grey area drain into right lymphatic duel
- •I saw them walking along the street.
- •I saw Sydorenko running along the avenue.
- •III. Independent Work: Disorders of Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Tissue
- •In inflammation of the lymphatic vessels called lymphangitis, red streaks can be seen extending along an extremity. Septicemia or blood poisoning may occur because of streptococci.
- •1. Вона бачила через вікно, що йшов сильний дощ. 2. Він хотів, щоб пацієнт одужав швидше. 3. Ти вже маєш переписаний текст? 4. Медсестра вже зробила перев'язку.
- •Irritants can be bacteria, friction, chemicals, X-rays, fire, cuts or blows, etc.
- •Immunity is the power of an individual to resist or overcome the effects of a particular disease or other harmful agents.
- •I. Speaking: Respiratory System
- •1. Pulmonary ventilation is normally accomplished by inspiration and expiration.
- •2. The diffusion of gases includes the passage of oxygen from air sacs into the blood andof carbon dioxide out of the blood.
- •3. The transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide by the circulating blood.
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Lungs
- •In infants the lungs are of a pale rosy color, but later they become darker.
- •1. Make your analyses of blood and urine. 2. Take an electrocardiogram. 3. Your lungs should be X-rayed. 4. Go to your doctor and check your bp. 5. You need treatment. 6. You will be treated.
- •I. Speaking: Respiratory System Disorders
- •I am going to examine you.
- •1. This science studies the structure and shapeof the body and organs. Take part in respiration. A. Kidneys b. Bladders c. Lungs d. Limbs person? e. Muscles a- Ears
- •11. With the help of what do we auscultate a
- •III. Independent Work: Virus
- •I. SPeaking: Digestive System
- •Inner, serous, salivary, hard, exact (точний), vital, face, connective, pale, length, palate, coat, capacity, gland, layer.
- •Vermiform appendix
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •3. That portion of the alimentary tract which forms the large intenstine consists of thececum, colon and rectum.
- •4. The valve that divides the atrium and the ventricle of the right chamber is called thetricuspid valve.
- •1. The left atrium and ventricle connected by the mitral valve form the left chamber of theheart.
- •In the pulmonological department there are patients with lung diseases. They suffer from pneumonia, bronchitis, asthma, etc. They complain of their bad cough, high temperature, headache.
- •I feel faint. - Мені погано.
- •Infection with the bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
- •Home Treatment
- •1. What function does the process of digestion 3. Where does food get in at first?fulfill? a. The large intestine
- •1. A) The discussion of the report lasted two hours.
- •I. Speaking: Nervous System (Part I)
- •(Part I)
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •It's no use crying over spilt milk.
- •I was afraid of being here in such hour.
- •10. Sterilizing the instruments, preparing the patient for the operation took me about an hour.
- •4.1 Was told that he was operated on without having been anesthetized.
- •5. After having gathered a complete clinical history, he began to examine the patient.
- •III. Independent Work: Role of Nervous System
- •It should be remembered that unlike animals, man can himself considerably change his external environment.
- •I. Pavlov demonstrated that man's so-called psychic activity is based on physiological processes operating in the cerebral cortex.
- •I. Speaking: Nervous System (Part II)
- •The functions of the autonomic nervous system.
- •31 Pairs of spinal nerves, each pair is numbered according to the level of the spinal cord from which it arises. Each spinal nerve has small posterior divisions and rather large anterior divisions.
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •1. There is no hope of our seeing him soon.
- •1) Dura mater is the upper layer, the outmost of the three membranes, which surrounds the spinal cord and is the toughest and most fibrous substance.
- •1. Special sensory impulses, such as those for smell, taste, vision, and hearing.
- •2. General sensory impulses, such as those for pain, touch, temperature, deep musclesense, pressure, and vibration.
- •3. Somatic motor impulses, resulting in voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
- •4. Visceral motor impulses producing involuntary control of glands and muscles of theheart and smooth muscles.
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •1 The first faculty to go and the last to appear - здатність, що першою зникає і останньою з'являється
- •1. What is cts? 2. What does the method of mri mean? 3. What is eeg? 4. What can we study with the help of the electroencephalograph?
- •Tumors of the brain are growths of brain tissues and meninges of abnormal character.
- •III. Independent Work: Pain
- •1. How can pain be relieved? 2. Can pain be localized? 3. Where are receptors for pain distributed? 4. What are nociceptors? 5. Is pain the most primitive sensation?
- •I. Speaking: Sensory System
- •Vision from receptors in the eye.
- •1. What system is responsible for all activitiesof organs and systems of organs in the humanbody?
- •10. He dared test this device without permission.11.1 cannot understand why you should do it.
- •III. Independent Work: Drugs
- •1 Awareness [s'wesnss] свідомість, усвідомлення
- •I. Speaking: Endocrine System
- •Islets of Langcrhans (in pancreas)
- •What are the parts of the endocrine system?
- •1. What substances are produced by endocrineglands?
- •1. Some glands practically limit their activity to this.
- •2. The activity of a gland is normally accompanied by a great dilation of its bloodvessels.
- •I. Speaking: Urinary System
- •10. What disorders of the urinary system do you know?
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •Vulva is the external genitalia, it includes the vaginal lips, clitoris and vaginal and urethral orifices. The space between the vaginal orifice and the anus is called perineum.
- •Is the placenta also an organ?
- •I. Speaking: Duties of a Midwife
- •In what ways does Nicky prepare women for birth in her weekly antenatal classes?
- •II. Independent Work: Risk of Having Children in Later Life
- •Symptoms
- •In the second trimester, the uterus expands, abdominal enlargement becomes more apparent, and the woman can feel the fetus move. Many women feel their best during this trimester.
- •Immunization against chickenpox
- •Immunization against hepatitis в if you are at increased risk of getting this infection;
- •Illegal drugs;
- •1) Fertility; 2) in vitro; 3) menopause; 4) to fail; 5) to insert; 6) to increase.
- •II. Independent Work: Miscarriage
- •I. Speaking: Precautions
- •It is estimated - приблизно підраховано inherited predisposition - спадкова схильність contemplate - обдумувати; мати намір to be vulnerable - бути вразливим ingestion - ковтання, поглинання
- •I. Speaking: Fetus
- •Vary - різнитися, мінятися
- •II. Independent Work: Premature Delivery
- •I. Speaking: Labor
- •3. And sleepiness are common.
- •II. Independent Work: who. Pandemics and Tamif lu
- •Improving sanitation and water supply,
- •Deaths per day. We have lost many nurses and doctors. Special trains carry away the dead. For several days there were no coffins and the bodies piled up."
- •Viruses reproduce outside your body.
- •I Speaking
- •I. Speaking: Anesthesia
- •1. How do anesthetic drugs work?
- •2. Why do you think patients were held or strapped down before anesthetic drugs wereavailable?
- •3.What difference did anesthetic drugs make to the work of surgeons?
- •2. Read and translate the text.
- •II. Grammar Exercises
- •III. Independent Work: Major Medical Specialty Fields
- •I. Speaking: English Prescription
- •1. Name and address of the physician and his telephone number. The title m.D. (MedicalDoctor) should follow the physician's name to indicate that he or she is a physician.
- •2. Usually at the top - patient's name, address, age and the date.
- •3. Symbol Rx. This is about the same as "Dear Sir" on top of a letter. It comes from Latinand means a command for a patient "you take".
- •4. The body of the prescription contains the name of the drag and the dose.
- •5Is copy right - на неї (назву) розповсюджується авторське право 6to capitalize - писати з великої літери 7it goes without saying - нічого й говорити 8dose specification - інструкція з дозування
- •230 Broad Street
- •1. Dioscorides, a Greek physician of the second century who accompanied the Romanarmies
- •In his estate he cultivated his orchard and worked there being in old age.
- •13 Sliding palpation - ковзна пальпація
- •14 To win (won) recognition - здобути визнання
- •1 Disaster [di'za:sts] катастрофа, лихо
- •1 Sensor ['sensa] an instrument which reacts to certain physical conditions or impressions such as beat, and which is used to provide information
- •2 Set up [set'Apj here, make the necessary preparations for something to be used in a certain way
- •3 Quality control ['kwolitikan'traul] activity of checking that products are all of a satisfactory standard
- •4 Batch [bsetf] group of things or people
- •§ 1. Спонукальні речення
- •§ 2. Відмінювання іменників і займенників
- •§ 3. Множина іменників (вимова)
- •§ 4. Артикль
- •§ 5. Наказові речення (інтонація)
- •§ 6. Рід іменників
- •§ 7. Дієслова to be, to have у часах групи Indefinite
- •§ 8. Множина іменників (способи утворення, правопис)
- •§ 9. Вказівні займенники this - цей, ця, це these - ці that - той, та, те those - ті such - такий the same - той самий
- •§ 10. Загальне питання та його інтонація
- •§ 11. Особливості однини та множини іменників
- •§ 12. Множина іменників латинського і грецького походження
- •§ 13. Альтернативні питання та їх інтонація
- •§ 14. Особові займенники
- •§15. Прийменники місця і напрямку
- •§ 16. Спеціальні питання
- •§ 17. Питальні слова
- •§ 18. Присвійні займенники
- •§ 19. Прийменниковий додаток
- •§ 20. Родовий відмінок іменника
- •§ 21. Слова, що замінюють артиклі
- •§ 22. Дієслово у Present Simple (Теперішній неозначений час)
- •§ 23. Порядок слів у стверджувальному розповідному реченні
- •§ 24. Слова-замінники іменника:
- •§ 25. Третя особа однини дієслова у Present Indefinite
- •§ 26. Прислівники неозначеного часу
- •§ 27. Спеціальні питання до підмета та його означення
- •§ 28. Ланцюг іменників (правило ряду)
- •§ 29. Звороти there is/are
- •§ 31. Парні сполучники
- •§ 32. Об'єктний відмінок особових займенників
- •§ 33. Основні форми дієслова
- •§ 34. Вживання займенника it
- •§ 35. Вживання слів much - many, little - few
- •§ 36. Питальна і заперечна форма дієслова у Present Simple
- •§ 37. Схеми загального і спеціального питань
- •§ 38. Присвійний відмінок іменників
- •§ 39. Числівники
- •§ 49. Неозначені займенники some, any
- •2. Порядкові числівники.
- •3. Дроби,
- •§ 40. Конверсія
- •§ 41. Місце прямого і непрямого додатків у реченні
- •§ 42. Дієслово у Past Indefinite (Минулий неозначений час)
- •§ 44. Дієслово to be у Past Indefinite Теперішній час Минулий
- •§ 45. Дати, місяці, дні тижня
- •§ 46. Participle II (Past Participle) (Дієприкметник минулого часу)
- •§ 47. Дієслово to have і зворот to have got
- •§ 48. Вираження відмінків у реченні
- •§ 49. Неозначені займенники some, any
- •§ 50. Зворотні займенники
- •§ 51. Модальне дієслово сап і вирази, що його замінюють
- •§ 52. Способи перекладу слова as
- •§ 53. Пасивний стан дієслова
- •§ 54. The Present Simple and Present Continuous Tenses (Теперішній неозначений та теперішній тривалий часи)
- •§ 55. Способи перекладу слова one
- •§ 57. Дієслово у Past Simple, Past Continuous (Минулий неозначений та тривалий часи)
- •§ 58. Infinitive (Інфінітив)
- •§ 59. Прийменники і сполучники часу
- •§ 60. Зворот to be going to
- •§ 61. Дієслово у Future Simple, Future Continuous (Майбутній неозначений та тривалий часи)
- •§ 62. Питально-заперечні речення
- •§ 63. Дієслово у Present Perfect (Теперішній завершений час)
- •§ 64. Вживання Present Perfect
- •§ 65. Складнопідрядні означальні речення
- •3. Схема безсполучникового підрядного означального речення:
- •I had rung him up before I went home. (я подзвонив йому перед тим, як пішов додому.)
- •§ 69. Підсилювальна конструкція it's... That (who)
- •§ 70. Узгодження часів (Sequence of Tenses)
- •§ 71. Розділові запитання (Disjunctive Questions)
- •§ 72. Висловлення прохання чи наказу першій чи третій особі
- •§ 73. Дієслово у Future Continuous (Майбутній тривалий час)
- •I shall be doing exercises tomorrow morning. (я робитиму вправи завтра вранці.)
- •I'll be speaking to you again at 5 tomorrow. (я переговорю з тобою знову о 5й завтра.) I shall be working when my sister visits me. (Коли моя сестра прийде до мене, я буду працювати.)
- •§ 74. Передача наказу чи прохання у непрямій мові
- •§ 75. Підрядні речення наслідку
- •§ 76. Непряма мова (Indirect Speech)
- •§ 77. Непрямі питання (indirect Questions) Загальне питання:
- •§ 79. Ступені порівняння прикметників (Degrees of Comparison)
- •§ 80. Безособові речення (Impersonal Sentences)
- •§ 81. Дієслово у Future-in-the-Past Indefinite (Майбутній час з точки зору минулого)
- •4. Пасивний стан:
- •§ 84. Ступені порівняння прислівників (Degrees of Comparison of Adverbs)
- •§ 93. Скорочені стверджувальні і заперечні речення типу
- •§ 94. Місце прислівників у реченні
- •§ 95. Infinitive (Інфінітив, неозначена форма дієслова)
- •§ 96. Функції інфінітива в реченні
- •§ 97. Objective Infinitive Complex (Об'єктний інфінітивний комплекс)
- •§ 98. Subjective Infinitive Complex (Суб'єктний інфінітивний комплекс)
- •§ 99. Prepositional Infinitive Complex (Інфінітивний прийменниковий комплекс)
- •§ 100. Особливості перекладу інфінітивних комплексів
- •§ 101. Participle (I) (Present), Participle II (Past), Perfect Participle (Дієприкметники)
- •Що формує, формувальний
- •§ 102. Значення й вживання дієприкметників
- •§ 103. Objective Participial Construction (Об'єктний дієприкметниковий комплекс
- •§ 104. Subjective Participial Construction (Суб'єктний дієприкметниковий комплекс)
- •§ 105. Absolute Participle Complex (Незалежний дієприкметниковий комплекс)
- •§ 106, Gerund (Герундій)
- •§ 107. Вживання герундія
- •§ 108. Gerund Constructions (Комплекси з герундієм)
- •§ 109. Переклад комплексів із герундієм
- •§ 110. Gerund and Verbal Noun (Герундій та віддієслівний іменник)
- •§ 111. Conditional Clauses (Підрядні умовні речення)
- •§ 112. Subjunctive Mood (Умовний спосіб)
- •§ 113. Conjunction (Сполучник)
- •§ 114. Складені прийменники та сполучники
- •Додаток 2 modal verbs (модальні дієслова)
Visceral ['visaral] що стосується нутрощів
subserous [sAb'siares] підсерозний
extend [iks'tend] простягатись
upward [Apwad] вгору
level [levl] рівень
Vary ['veari] мінятись; змінюватись
proper ['ргора] правильний, відповідний; властивий, притаманний
Exercise 9. Fill in the blanks, use the words: varies, covered, extends, heavier. 1. The aorta ... from the upper part of the left ventricle. 2. The shape of the vessels .. they dilate. 3. The right lung is ... than the left one. 4. The lungs are ... with the pleura.
-.7. usual during emotiona. : On physical exertion the
T'r.e heart acts as a pumr :- :ons of blood are pumpec . was the first scientist te
rtention to their Latin/Greek
Ukrainian
ерія
черюла
■ апілярна судина
extends, heavier. rape of the vessels ... whe: ... with the pleura.
Exercise 10. Read the text, translate it.
Blood Vessels and Blood Circulation
The blood vessels together with the four heart chambers form a closed system for the flow of blood. They are divided into three groups: arteries carry blood from the ventricles (pumping chambers) of the heart out to the capillaries in the tissues (the smallest arteries are called arterioles); veins drain capillaries in the tissues and return the blood to the heart (the smallest veins are called venules); capillaries allow for exchanges between the blood and body cells or between the blood and air in the lung tissues. The capillaries connect the arterioles and venules. Aorta is the largest artery with thick walls because it receives blood under the highest pressure from the left ventricle.
All vessels together make up two circuits: pulmonary and systemic. Pulmonary vessels carry blood to and from the lungs. Systemic arteries and veins serve the rest of the body, supplying nutrients and oxygen to all the tissues and carry away waste materials from the tissues for disposal (Fig. 12-1).
We know that the venous blood from the systemic and portal circulation is brought to the right atrium of the heart. When the pressure in the right atrium has increased, the blood passes into the right ventricle from the right atrium.

During
the systole of the ventricle the blood is pumped from the right
ventricle into the pulmonary artery. When the right ventricle has
pumped the venous blood into the pulmonary artery, it enters the
pulmonary circulation. The blood is brought to the lungs through the
pulmonary artery. In the lungs the venous blood discharges carbon
dioxide. When the blood has discharged carbon dioxide, it takes in
oxygen in the lungs.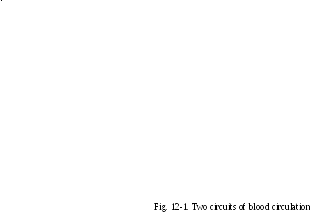
The blood, which has become oxygenated, passes from the enous part of the pulmonary capillary system into the veins, and venules. When the oxygenated blood has passed the four pulmonary veins, it is brought to the left atrium of the heart.
Under the pressure in the left atrium the arterial blood, a hich the pulmonary veins have brought to the heart, is pumped :nto the left ventricle. During the prolonged contraction of the eft ventricle, the so-called ventricular systole, the arterial blood s pumped into the aorta. When the left ventricle has pumped the arterial blood into the aorta, it is carried through the arteries to all ".he parts of the body.
We can control the work of our heart feeling the pulse. It is :he wave of pressure that travels along the arteries as ventricles contract (about 70-80 times per minute). The pulse can be felt in any artery that is relatively close to the surface. We can only press ::ie vessel down against a bone. Usually we feel the pulse on the "adial artery on the wrist.
Blood pressure (BP) is the force exerted by the blood -gainst the walls of the vessels. We measure BP with the help of sphygmomanometer [^sfigmsumq'nrjmita], and two variables are measured: systolic, which occurs during heart muscle contraction,
and diastolic, which occurs during relaxation of the heart muscle. The normal BP in adults is 120 to 80 mm Hg.
Exercise 11. Find English equivalents in the text.
Легеневе коло кровообігу, несуть кров до і від легенів, постачаючи поживними речовинами, повертають кров до серця, найвищий тиск, виштовхується з правого шлуночка до легеневої артерії, коли шлуночки скорочуються, можна відчути, просто притиснути, виміряти кров'яний тиск, що з'являється під час розслаблення.
Exercise 12. Read the following sentences and say what they are about.
1. This part of the heart discharges the blood received from the pulmonary circulation through the aorta to the systemic circulation. 2. This part of the heart discharges the blood received from the systemic circulation to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries.
Exercise 13. Read the list of disorders involving the blood vessels. Try to memorize these diseases.
Hypertension (high BP).
Hypotension (low BP).
Aneurysm (weakness of vessels).
Arterial degeneration:
- atherosclerosis (fatty deposits in vessels, may result in thrombus);
- arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries with scar tissue or calcium salts, may result in ischemia and cell necrosis).
Hemorrhage (massive loss of blood).
Shock (inadequate output of blood from the heart).
Varicose veins (swelling of veins in legs and rectum).
Phlebitis (inflammation of a vein).
Embolus (a piece of clot travelling in the circulation). 10.Pulmonary embolism (a clot lodged in lungs).
Control Tests. Cardiovascular System
1. We check BP with
A. cardiogram
B. tonometer
C. stethoscope
D. fingers
E. palpation
3. Between the right and left heart there is
A. an artery
B. a vessel
C. a septum
D. a valve
E. a wall
2. The greater circulation begins with
A. the right heart
B. the left ventricle
C. the right atrium
D. the right ventricle
E. the left atrium
4. Between the chambers in the heart there are
A. valves
B. boxes
C. walls
D. septa
E. vessels
5 The heart has chambers.
A. two
B. three
C. four
D. six
E. eight
n. Where isn't the heart situated?
A. In the chest
B. In the left part of the thorax
C. In the right part of the thorax
D. Above the diaphragm
E. Between the lungs
~. What part doesn't belong to the heart?
A. Chamber
B. Atrium
C. Valve
D. Stomach
E. Ventricle
S. How many blood circulations are there in the human body?
A. 3
B.4
C. 5
D. 2
E. 6
3. What science studies the diseases of the heart and blood vessels?
A. Pathology
B. Biology
C. Cardiology
D. Genetics
E. Physiology
10. What valve is there between the left atrium and ventricle?
A. Tricuspid
B. Aortic
C. Venous
D. Mitral
E. Arterious
11. How do we call the valve between theright atrium and ventricle?
A. Tricuspid
B. Aortic
C. Mitral
D. Venous
E. Arterious
12. How many ventricles does the humanheart have?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 1E.No
13. The heart and blood vessels form the .
A. digestive system
B. nervous system
C. urinary system
D. cardiovascular systemC. endocrine system
14. Hypertension is the .
A. low BP
B. high BP
C. atonia
D. dystonia
E. lack of vitamins
15. A red blood cell is .
A. leukocyte
B. monocyte
C. phagocyte
D. erythrocyte
E. granulocyte
16. There are groups of blood.
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
E. 6
17. The largest arterial vessel is .
A. artery
B. vein
C. capillary
D. aorta
E. membrane
18. What medicine is used to prevent theformation of blood clots?
A. Anticoagulant
B. Digitalis
C. Nitroglycerine
D. Menthol
E. Sedative
19. Leukocytes are blood cells.
A. red
B. green
C. white
D. blue
E. yellow
20. The heart cycle is .
A. tachycardia and bradycardia
B. tachycardia and hypotension
C. systole and diastole
D. tachypnea and dyspnea
E. spasm and relaxation
21. What is the universal group of blood?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
22. How do we call the person who gives his blood to another person?
A. Recipient
B. Patient
C. Doctor
D. Visitor
E. Donor
23. What does hemopoiesis mean?
A. Formation of blood
B. Formation of cells
C. Formation of urine
D. Formation of energy
E. Formation of lymph
24. What is the synonym of thrombocytus!
A. Hemoglobin
B. Protein
C. Platelet
D. Blood clotting
E. Plasma
25. What doesn't belong to the organs of th;cardiovascular system?
A. Spleen
B. Heart
C. Pancreas
D. Liver
E. Blood vessels
26. What is the role of valves in the heart?
A. To pump the blood from the heart
B. To prevent flow of blood into \:.-.atrium
C. To promote contractions of the hear
D. To promote relaxation of the heart
E. To make beatings of the heart
27. The middle, the thickest layer of t':.-.cardiac wall is .
A. pericardium
B. endocardium
C. cardiac membrane
D. cardiac sack
E. myocardium
28. What is the other name of the lesser bk :.circulation?
A. Pulmonary
B. Cardiac
C. Gastric
D. Cervical
E. Thoracic
29. When the blood is given from one personto the other, it is .
A. presenting
B. injecting
C. suffering
D. transfusing
E. carrying
30. The science which studies the causes ofdiseases.
A. Etiology
B. Pathology
C. Psychology
D. Cardiology
E. Cytology
31. What does the blood receive in the lungs?
A. Vitamins
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Hemoglobin
D. Oxygen
E. Bacteria
32. What blood comes into the left heart?
A. Venous
B. Arterial
C. Oxygenated
D. Dark red
E. Scarlet
33. What is the normal blood pressure ofyoung people?
A. 130 over 90
B. 120 over 80
C. 150 over 100
D. 140 over 90
E. 200 over 110
34. What does the heart pump?
A. Plasma
B. Lymph
C. Urine
D. Water
E. Blood
35. What is the normal heartbeat in adults?
A. About 60-70 beats per minute
B. About 100 beats per minute
C. About 110 beats per minute
D. About 60-70 beats per hour
E. About 50 beats per minute
36. Where do we usually check the pulse?
A. Over the radial artery
B. Over the temporal bone
C. Over the knee
D. Over the elbow
E. Over the cardiac area
37. The blood of greater circulation returns tothe heart by means of .
A. arteries
B. veins
C. lungs
D. vessels
E. mechanisms
38. The person to whom the blood is given.
A. Doctor
B. Nurse
C. Obstetrician
D. Donor
E. Recipient
39. The pulmonary circulation begins with .
A. the left heart
B. the right ventricle
C. the right atrium
D. the left ventricle
E. the left atrium
40. The blood cell has no .
A. enzymes
B. leukocytes
C. platelets
D. erythrocytes
E. plasma
41. The function of the blood doesn't include
A. regulation of body temperature
B. transporting nutrients to cells
C. production of hormones
D. immunization against foreign particles
E. supplying oxygen to cells
42. The inflammation of veins is .
A. arthritis
B. chondritis
C. phlebitis
D. cystitis
E. carditis
43. The blood vessels which have the
lowest BP.
A. Arterioles
B. Venules
C. Capillaries
D. Arteries
E. Veins
44. When body temperature is 1 ° higher, thepulse rate is faster.
A. 2-3 beats
B. 4-6 beats
C. 7-8 beats
D. 1-2 beats
E. 8-10 beats
45. What does arterial pressure mean?
A. Pressure on the arterial walls
B. Pressure on the venous walls
C. Pressure on the capillary walls
D. Pressure on the vessel walls
E. Pressure on the walls of the heart
46. What symptom isn't characteristic ofcardiovascular diseases?
A.headache
B. heartache
C. sneezing
D. stomachache
E. cough
47. What information is given in thetemperature chart?
A. Pulse. t°, BP
B. Pulse. t°
C. t°, BP
D. Pulse, BP
E. Only t°
48. What is bradycardia?
A. Slower heart rate
B. Normal heart rate
C. Faster heart rate
D. Work of the heart during sleep
E. Work of the heart after exercises
49. What is tachycardia?
A. Slower heart rate
B. Normal heart rate
C. Faster heart rate
D. Work of the heart during sleep
E. Work of the heart after exercises
50. What does the term "arythmia" mean?
A. Slower heartbeat
B. Normal heartbeat
C. Faster heartbeat
D. Absence of heartbeat
E. Changes in heartbeat
il. Grammar Exercises
Exercise 1. Form adjectives using the suffix -able, translate them.
Consider, change, depend, vary, eat, question, work.
Exercise 2. Name and translate the verbs from which the following nouns are formed.
Operation, circulation, estimation, radiation, location, separation, graduation, dilation, regulation.
Exercise 3. Insert already or yet. Translate the following sentences.
1. Scientists have introduced this term. 2. Researchers have not found out the origin of this disease. 3. Physiologists have estimated the importance of this great discover}'. 4. They have not published the book on their discoveries.
Exercise 4. Put the verbs into the correct form. Translate the following sentences.
1. The nurse already (to take temperature). 2. The doctor not (to use) this method of treatment. 3. She not (to see) her parents since May. 4. The nurse just (to determine) the patient's blood group.
Exercise 5. Choose the right answer.
1. Did scientists find out the total weight of the blood?
Scientists find out the total weight of the blood.
Scientists found out the total weight of the blood.
Total weight of the blood was found out by the scientists.
2. Is the rate of heartbeat regulated by two groups of nerve fibers?
The rate of heartbeat will be regulated by two groups of nerve fibers.
Two groups of nerve fibers have regulated the rate of heartbeat.
The rate of heartbeat is regulated by two groups of nerve fibers.
Exercise 6. Read the following sentences. Translate them paying attention to the words in bold type.
Will you bring me your notes on anatomy?
The venous blood is brought to the right atrium of the heart.
The chemical formula of carbon dioxide is CO,.
The chemical formula of oxygen is О .
Oxygen is necessary for life.
To oxygenate means to enrich with oxygen.
The venous blood is oxygenated in the lungs.
The normal atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg.
Exercise 7. Form present, past and perfect participles from the following verbs. Give all types of their translation:
to restore, to introduce, to establish, to connect, to receive, to carry.
Exercise 8. Translate the following sentences, state the functions of participles in them.
The arterial blood coming from the lung is rich in oxygen.
Examining the patient the doctor asked him about his complaints.
Having bandaged the patient's arm, the nurse helped him to dress.
Being operated on, he didn't feel any pain.
The question discussed was very important for him.
When sent to the hospital he recovered soon.
