
- •Preface
- •About This Book
- •Acknowledgments
- •Contents at a Glance
- •Contents
- •Relaxing at the Beach
- •Dressing the Scene
- •Animating Motion
- •Rendering the Final Animation
- •Summary
- •The Interface Elements
- •Using the Menus
- •Using the Toolbars
- •Using the Viewports
- •Using the Command Panel
- •Using the Lower Interface Bar Controls
- •Interacting with the Interface
- •Getting Help
- •Summary
- •Understanding 3D Space
- •Using the Viewport Navigation Controls
- •Configuring the Viewports
- •Working with Viewport Backgrounds
- •Summary
- •Working with Max Scene Files
- •Setting File Preferences
- •Importing and Exporting
- •Referencing External Objects
- •Using the File Utilities
- •Accessing File Information
- •Summary
- •Customizing Modify and Utility Panel Buttons
- •Working with Custom Interfaces
- •Configuring Paths
- •Selecting System Units
- •Setting Preferences
- •Summary
- •Creating Primitive Objects
- •Exploring the Primitive Object Types
- •Summary
- •Selecting Objects
- •Setting Object Properties
- •Hiding and Freezing Objects
- •Using Layers
- •Summary
- •Cloning Objects
- •Understanding Cloning Options
- •Mirroring Objects
- •Cloning over Time
- •Spacing Cloned Objects
- •Creating Arrays of Objects
- •Summary
- •Working with Groups
- •Building Assemblies
- •Building Links between Objects
- •Displaying Links and Hierarchies
- •Working with Linked Objects
- •Summary
- •Using the Schematic View Window
- •Working with Hierarchies
- •Setting Schematic View Preferences
- •Using List Views
- •Summary
- •Working with the Transformation Tools
- •Using Pivot Points
- •Using the Align Commands
- •Using Grids
- •Using Snap Options
- •Summary
- •Exploring the Modifier Stack
- •Exploring Modifier Types
- •Summary
- •Exploring the Modeling Types
- •Working with Subobjects
- •Modeling Helpers
- •Summary
- •Drawing in 2D
- •Editing Splines
- •Using Spline Modifiers
- •Summary
- •Creating Editable Mesh and Poly Objects
- •Editing Mesh Objects
- •Editing Poly Objects
- •Using Mesh Editing Modifiers
- •Summary
- •Introducing Patch Grids
- •Editing Patches
- •Using Modifiers on Patch Objects
- •Summary
- •Creating NURBS Curves and Surfaces
- •Editing NURBS
- •Working with NURBS
- •Summary
- •Morphing Objects
- •Creating Conform Objects
- •Creating a ShapeMerge Object
- •Creating a Terrain Object
- •Using the Mesher Object
- •Working with BlobMesh Objects
- •Creating a Scatter Object
- •Creating Connect Objects
- •Modeling with Boolean Objects
- •Creating a Loft Object
- •Summary
- •Understanding the Various Particle Systems
- •Creating a Particle System
- •Using the Spray and Snow Particle Systems
- •Using the Super Spray Particle System
- •Using the Blizzard Particle System
- •Using the PArray Particle System
- •Using the PCloud Particle System
- •Using Particle System Maps
- •Controlling Particles with Particle Flow
- •Summary
- •Understanding Material Properties
- •Working with the Material Editor
- •Using the Material/Map Browser
- •Using the Material/Map Navigator
- •Summary
- •Using the Standard Material
- •Using Shading Types
- •Accessing Other Parameters
- •Using External Tools
- •Summary
- •Using Compound Materials
- •Using Raytrace Materials
- •Using the Matte/Shadow Material
- •Using the DirectX 9 Shader
- •Applying Multiple Materials
- •Material Modifiers
- •Summary
- •Understanding Maps
- •Understanding Material Map Types
- •Using the Maps Rollout
- •Using the Map Path Utility
- •Using Map Instances
- •Summary
- •Mapping Modifiers
- •Using the Unwrap UVW modifier
- •Summary
- •Working with Cameras
- •Setting Camera Parameters
- •Summary
- •Using the Camera Tracker Utility
- •Summary
- •Using Multi-Pass Cameras
- •Creating Multi-Pass Camera Effects
- •Summary
- •Understanding the Basics of Lighting
- •Getting to Know the Light Types
- •Creating and Positioning Light Objects
- •Viewing a Scene from a Light
- •Altering Light Parameters
- •Working with Photometric Lights
- •Using the Sunlight and Daylight Systems
- •Using Volume Lights
- •Summary
- •Selecting Advanced Lighting
- •Using Local Advanced Lighting Settings
- •Tutorial: Excluding objects from light tracing
- •Summary
- •Understanding Radiosity
- •Using Local and Global Advanced Lighting Settings
- •Working with Advanced Lighting Materials
- •Using Lighting Analysis
- •Summary
- •Using the Time Controls
- •Working with Keys
- •Using the Track Bar
- •Viewing and Editing Key Values
- •Using the Motion Panel
- •Using Ghosting
- •Animating Objects
- •Working with Previews
- •Wiring Parameters
- •Animation Modifiers
- •Summary
- •Understanding Controller Types
- •Assigning Controllers
- •Setting Default Controllers
- •Examining the Various Controllers
- •Summary
- •Working with Expressions in Spinners
- •Understanding the Expression Controller Interface
- •Understanding Expression Elements
- •Using Expression Controllers
- •Summary
- •Learning the Track View Interface
- •Working with Keys
- •Editing Time
- •Editing Curves
- •Filtering Tracks
- •Working with Controllers
- •Synchronizing to a Sound Track
- •Summary
- •Understanding Your Character
- •Building Bodies
- •Summary
- •Building a Bones System
- •Using the Bone Tools
- •Using the Skin Modifier
- •Summary
- •Creating Characters
- •Working with Characters
- •Using Character Animation Techniques
- •Summary
- •Forward versus Inverse Kinematics
- •Creating an Inverse Kinematics System
- •Using the Various Inverse Kinematics Methods
- •Summary
- •Creating and Binding Space Warps
- •Understanding Space Warp Types
- •Combining Particle Systems with Space Warps
- •Summary
- •Understanding Dynamics
- •Using Dynamic Objects
- •Defining Dynamic Material Properties
- •Using Dynamic Space Warps
- •Using the Dynamics Utility
- •Using the Flex Modifier
- •Summary
- •Using reactor
- •Using reactor Collections
- •Creating reactor Objects
- •Calculating and Previewing a Simulation
- •Constraining Objects
- •reactor Troubleshooting
- •Summary
- •Understanding the Max Renderers
- •Previewing with ActiveShade
- •Render Parameters
- •Rendering Preferences
- •Creating VUE Files
- •Using the Rendered Frame Window
- •Using the RAM Player
- •Reviewing the Render Types
- •Using Command-Line Rendering
- •Creating Panoramic Images
- •Getting Printer Help
- •Creating an Environment
- •Summary
- •Creating Atmospheric Effects
- •Using the Fire Effect
- •Using the Fog Effect
- •Summary
- •Using Render Elements
- •Adding Render Effects
- •Creating Lens Effects
- •Using Other Render Effects
- •Summary
- •Using Raytrace Materials
- •Using a Raytrace Map
- •Enabling mental ray
- •Summary
- •Understanding Network Rendering
- •Network Requirements
- •Setting up a Network Rendering System
- •Starting the Network Rendering System
- •Configuring the Network Manager and Servers
- •Logging Errors
- •Using the Monitor
- •Setting up Batch Rendering
- •Summary
- •Compositing with Photoshop
- •Video Editing with Premiere
- •Video Compositing with After Effects
- •Introducing Combustion
- •Using Other Compositing Solutions
- •Summary
- •Completing Post-Production with the Video Post Interface
- •Working with Sequences
- •Adding and Editing Events
- •Working with Ranges
- •Working with Lens Effects Filters
- •Summary
- •What Is MAXScript?
- •MAXScript Tools
- •Setting MAXScript Preferences
- •Types of Scripts
- •Writing Your Own MAXScripts
- •Learning the Visual MAXScript Editor Interface
- •Laying Out a Rollout
- •Summary
- •Working with Plug-Ins
- •Locating Plug-Ins
- •Summary
- •Low-Res Modeling
- •Using Channels
- •Using Vertex Colors
- •Rendering to a Texture
- •Summary
- •Max and Architecture
- •Using AEC Objects
- •Using Architectural materials
- •Summary
- •Tutorial: Creating Icy Geometry with BlobMesh
- •Tutorial: Using Caustic Photons to Create a Disco Ball
- •Summary
- •mental ray Rendering System
- •Particle Flow
- •reactor 2.0
- •Schematic View
- •BlobMesh
- •Spline and Patch Features
- •Import and Export
- •Shell Modifier
- •Vertex Paint and Channel Info
- •Architectural Primitives and Materials
- •Minor Improvements
- •Choosing an Operating System
- •Hardware Requirements
- •Installing 3ds max 6
- •Authorizing the Software
- •Setting the Display Driver
- •Updating Max
- •Moving Max to Another Computer
- •Using Keyboard Shortcuts
- •Using the Hotkey Map
- •Main Interface Shortcuts
- •Dialog Box Shortcuts
- •Miscellaneous Shortcuts
- •System Requirements
- •Using the CDs with Windows
- •What’s on the CDs
- •Troubleshooting
- •Index
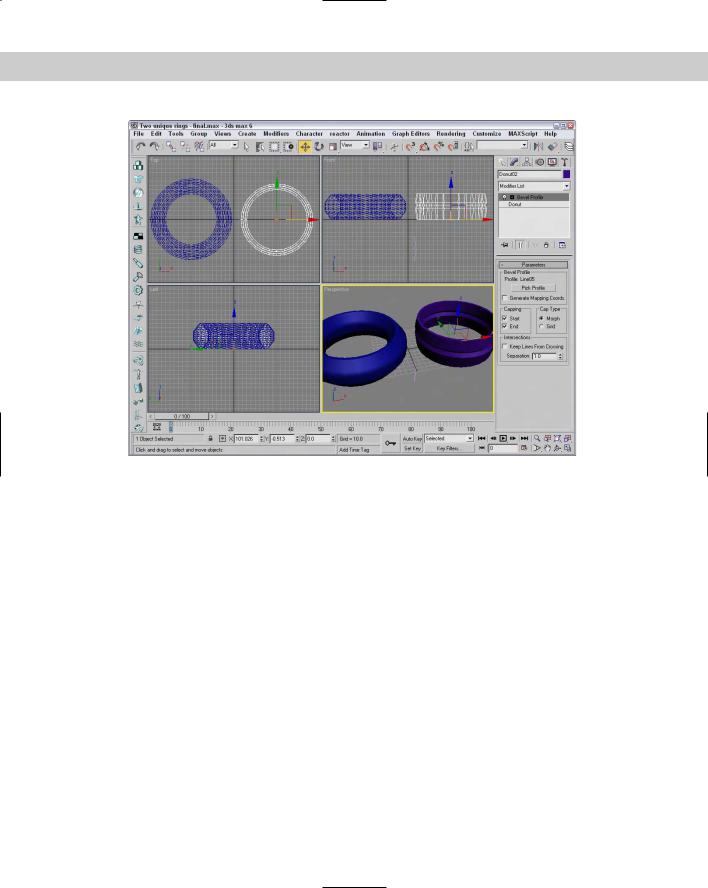
388 Part III Modeling
Figure 13-39: Bevels applied to a shape can give a unique profile edge.
Summary
As this chapter has shown, there is much more to splines than just points, lines, and control handles. Splines in Max are one of the fundamental building blocks and the pathway to advanced modeling skills using NURBS.
This chapter covered the following spline topics:
Understanding the various shape primitives
Editing splines
Working with the various spline subobjects
Applying modifiers to splines
The next chapter continues our voyage down the modeling pathway with perhaps the most common modeling types — meshes and polys.
|
|
|

Working with Meshes and Polys
Meshes, or — more specifically — polygon meshes, are perhaps the most popular and the default model type for most 3D
programs. You create them by placing polygonal faces next to one another so the edges are joined. The polygons can then be smoothed from face to face during the rendering process. Using meshes, you can create almost any 3D object, including simple primitives such as a cube converted to a mesh or a realistic dinosaur.
Meshes have lots of advantages. They are common, intuitive to work with, and supported by a large number of 3D software packages. In this chapter, you learn how to create and edit mesh and poly objects, and you also get experience using some mesh object modifiers.
Creating Editable Mesh
and Poly Objects
The Create panel has no method for making mesh objects — mesh objects must be converted from another object type or produced as the result of a modifier. Object types that you can convert include shapes, primitives, Booleans, patches, and NURBS. Many models that are imported appear as mesh objects. Most 3D formats, including 3DS and DXF, import as mesh objects.
Note You can even convert spline shapes to editable meshes, whether they are open or closed. Closed splines are filled with a polygon, whereas open splines are only a single edge and can be hard to see.
Before you can use many of the mesh editing functions discussed in this chapter, you need to convert the object to an Editable Mesh object or an Editable Poly object, collapse an object with modifiers applied, or apply the Edit Mesh modifier.
Converting objects
14C H A P T E R
In This Chapter
Creating Editable Mesh and Poly objects
Working with the mesh and poly subobject modes
Editing meshes and polys
Learning to use the different mesh modifiers
To convert an object into an Editable Mesh or an Editable Poly object, right-click the object and choose Convert To Convert to Editable Mesh or Convert to Editable Poly from the pop-up

390 Part III Modeling
quadmenu. You can also convert an object by right-clicking the object within the Modifier Stack and selecting one of the convert options from the pop-up menu.
Collapsing to a mesh object
When an object is collapsed, it loses its parametric nature and the parameters associated with any applied modifiers. Only objects that have had modifiers applied to them can be collapsed. Objects are made into an Editable Mesh object when you use the Collapse To option available from the right-click pop-up menu in the Modifier Stack or when you use the Collapse utility.
Tip |
You can also collapse objects using the Collapse utility found in the Utilities panel. |
Most objects collapse to Editable Mesh objects, but objects with the Select Poly modifier applied collapse to Editable Poly objects.
Applying the Edit Mesh modifier
Another way to enable the mesh editing features is to apply the Edit Mesh modifier to an object. You apply this modifier by selecting the object and choosing Modifiers Mesh Editing Edit Mesh, or selecting Edit Mesh from the Modifier drop-down list in the Modify panel.
The Edit Mesh modifier is different from the Editable Mesh object in that as an applied modifier, it maintains the parametric nature of the original object. For example, you cannot change the Radius value of a sphere object that has been converted to an Editable Mesh, but you could if the Edit Mesh modifier were applied.
Note |
There is no Edit Poly modifier. |
Editable Mesh versus Editable Poly objects
At this point, you may be asking yourself what the differences are between an Editable Mesh object and an Editable Poly object. Editable Mesh objects split all polygons into triangular faces, but the Editable Poly object maintains four-sided polygon faces. Another key difference is found in the subobjects. Editable Meshes can work with Vertex, Edge, Face, Polygon, and Element subobjects; and Editable Poly objects can work with Vertex, Edge, Border, Polygon, and Element subobjects.
The majority of features are the same for both Editable Mesh and Editable Poly objects, but some features are available only for one of these. These differences are highlighted in Table 14-1.
Note |
Many of the Editable Poly buttons have a Settings dialog box available. Clicking on the small |
|
icon to the right of the button opens a dialog box where you can interactively change the set- |
|
tings and see the results. All features in the Table 14-1 that have a Settings dialog box avail- |
|
able are indicated by an asterisk (*). |

Chapter 14 Working with Meshes and Polys 391
Table 14-1: Editable Mesh and Poly Features
Feature |
Editable Mesh |
Editable Poly |
|
|
|
Vertex, Edge, Polygon, and Element subobject modes |
X |
X |
Face subobject mode |
X |
|
Border subobject mode |
|
X |
Selection by Vertex, Ignore Backfacing |
X |
X |
Ignore Visible Edges, Planar Threshold, Show Normals |
X |
|
Hide/UnHide All |
X |
X |
Hide Unselected |
|
X |
Shrink, Grow, Ring, Loop Selection |
|
X |
Copy/Paste Named Selections |
X |
X |
Soft Selection |
X |
X |
Shaded Face Toggle |
|
X |
Repeat Last |
|
X |
Create |
X |
X |
Delete/Remove |
X |
X |
Attach/Attach List |
X |
X* |
Detach |
|
X |
Break |
X |
X |
Turn |
X |
|
Extrude |
X |
X* |
Bevel |
|
X* |
Chamfer |
|
X* |
Connect |
|
X* |
Split |
|
X |
Insert Vertex |
|
X |
Edit Triangulation/Retriangulation |
|
X |
Cap |
|
X |
Outline |
|
X* |
Inset |
|
X* |
Flip |
|
X |
Hinge from Edge |
|
X* |
Continued
